| 산스크리트어 | |
|---|---|
사스스크타 | |
 데바나가리 스크립트의 사스스크타 | |
발음 | [스크리타지트] |
| 지역 | 남아시아 동남아시아 일부 지역 |
시대 | c. 제 2 천년 기원전 – 600 기원전 (베다 산스크리트어); [1] 600 BCE – 현재 (고전 산스크리트어) |
| 부흥 | 인도의24,821명[2]과 네팔의1,669명[3]은 산스크리트어를 모국어로 등록했습니다. 인도산스크리트어의 총 연사수는 2,360,821명입니다. [4] |
초기 형태 | |
| 데바나가리어, 또한 다양한 다른 브라믹 스크립트로작성[5] | |
| 언어 코드 | |
| ISO 639-1 | sa |
| ISO 639-2 | san |
| ISO 639-3 | san |
| 글로트로그 | sans1269[6] |
산스크리트어 (영어: /이에 이에이븐nskr.îtt /; [7] 산스크리트어 : 로마자화: sa'skrta, IPA : [[들으세요] ![]() (듣기)3,500 년의 역사를 가진 고대 인도의 언어이다. [8][9][10] 그것은 힌두교의 주요 전례 언어와 힌두교 철학의 대부분의 작품의 주요 언어뿐만 아니라 불교와 자이니즘의주요 텍스트의 일부입니다. 산스크리트어는 그 변종과 수많은 방언으로 고대와 중세 인도의 언어 프랑카였다. [11][12][13] 초기 1천년 CE에서 불교와 힌두교와 함께 산스크리트어는 동남아시아로이주했으며, [14] 동아시아[15] 및 중앙아시아의 일부 ,[16] 이 지역에서 높은 문화와 지역 지배 엘리트의 언어로 부상했다. [17][18]
(듣기)3,500 년의 역사를 가진 고대 인도의 언어이다. [8][9][10] 그것은 힌두교의 주요 전례 언어와 힌두교 철학의 대부분의 작품의 주요 언어뿐만 아니라 불교와 자이니즘의주요 텍스트의 일부입니다. 산스크리트어는 그 변종과 수많은 방언으로 고대와 중세 인도의 언어 프랑카였다. [11][12][13] 초기 1천년 CE에서 불교와 힌두교와 함께 산스크리트어는 동남아시아로이주했으며, [14] 동아시아[15] 및 중앙아시아의 일부 ,[16] 이 지역에서 높은 문화와 지역 지배 엘리트의 언어로 부상했다. [17][18]
산스크리트어는 오래된 유도 아리아어입니다. [8] 인도-유럽 언어 가족의 가장 오래된 문서화 된 구성원 중 하나로서,[19][참고 1][참고 2] 산스크리트어는 인도 - 유럽 연구에서눈에 띄는 위치를 보유하고있다. [22] 그것은 그리스어와 라틴어,[8] 뿐만 아니라 히티트, 루비안, 올드 아베스타와 유럽, 서아시아, 중앙 아시아 와 남아시아에 역사적 의미를 가진 다른 많은 살아 있고 멸종 언어와 관련이있다. 그것은 프로토 - 인도 - 아리아어 언어,프로토 - 인도 - 이란어와 프로토 - 인도 - 유럽 언어에 언어 조상을 추적합니다. [23]
산스크리트어는 베다 산스크리트어로알려진 형태로 제 2 천년 기원전까지 추적 할 수 있습니다, 초기 알려진 구성으로 리그베다와. 고전 산스크리트어라는 더 세련되고 표준화 된 문법 형태는 파이니의 A의 A의 A와 함께 중반 1 천년 기원전에서 나타났다. [8] 산스크리트어, 반드시 고전 산스크리트어아니지만, 많은 Prakrit 언어의 루트 언어입니다. [24] 예로는 힌디어, 마라타어, 벵골어, 펀자브어, 구자라트어, 신디어, 카슈미르어, 쿠마오니, 가르왈리, 우르두어, 도그리어, 마이틸리, 콘카니어, 아삼세, 오디아, 네팔어와 같은 아대륙 딸 언어가 있다. 【25】[26][27]
산스크리트어 문학의 몸은 철학적, 종교적 텍스트뿐만 아니라 시, 음악, 드라마, 과학,기술 및 기타 텍스트의풍부한 전통을 포함한다. 고대 시대에 산스크리트어 조성물은 뛰어난 복잡성, 엄격함 및 충실도를 암기하는 방법에 의해 구두로 전달되었습니다. [28][29] 산스크리트어에서 가장 오래된 비문은 아요디야와 고순디 하티바다(치토르가르)에서발견된 몇 안 되는 기원전부터 발견되었다. [30][참고 3] 제1천년 CE에 기재된 산스크리트어 텍스트는 브라미 스크립트, 나가르리 스크립트,역사적인 남인도 스크립트와 그 파생 스크립트로 작성되었습니다. [34][35][36] 산스크리트어는 인도 헌법의 여덟 번째 일정에나열된 22 개 언어 중 하나입니다. 그것은 널리 힌두교와 찬송가와 찬송가 와 같은 일부 불교 관행에서 의식과 의식 언어로 사용되고 있습니다.
어표 및 명명 :[편집]
산스크리트어형형형용사에서 사우스크타-는 샘(함께, 좋고, 잘, 완성된)과 krta-(만든, 형성된, 일)로 구성된 복합 단어이다. [37][38] 그것은 "잘 준비되고, 순수하고, 완전하며, 세련되고, 성스러운" 사업을 나타낸다. [39][40][41] 비더만에 따르면, 문맥상 단어의 어원적 기원에서 언급되는 완벽함은 의미론적이라기보다는 그 색조이다. 소리와 구두 전송은 고대 인도에서 매우 가치있는 자질이었고, 그 현자는 알파벳, 단어의 구조와 "소리의 컬렉션, 숭고한 음악 금형의 일종"으로 정확한 문법을 정제, 그들은 산스크리트어라는필수적인 언어로 비더만 상태. [38] 베다 시대 후반부터 아네트 윌크와 올리버 모에버스는 공명하는 사운드와 음악적 기초를 인도에서 "매우 많은 양의 언어, 철학, 종교 문학"을 끌어들였다. 소리는 "모든 창조에 만연", 세계 자체의 또 다른 표현으로 시각화되었다; 힌두교 사상의 "신비한 매그넘". 생각의 완벽과 해방의 목표에 대한 탐구는 신성한 소리의 차원 중 하나였으며, 모든 아이디어와 영감을 엮은 공통의 실은 고대 인디언들이 완벽한 언어, 산스크리트어의 "포노센트 피스테미트"라고 믿는 것에 대한 탐구가 되었다. [42][43]
언어로서 산스크리트어는 프라크리틱 언어(prákta-)라는 수많은, 덜 정확한 언어 인도 언어와 경쟁했다. prakrta라는 용어는 문자 그대로 "원본, 자연, 정상, 예술"을 의미, 프랭클린 사우스 워스 상태. [44] 프라크리트와 산스크리트어의 관계는 1천년 CE에 일자 인도 문헌에서 발견된다. 파타냐리는 프라크리트(Prakrit)가 모든 불완전함을 가진 모든 어린이에게 본능적으로 입양된 첫 번째 언어이며, 나중에 는 해석과 오해의 문제로 이어진다고 인정했다. 산스크리트어의 정화 구조는 이러한 결함을 제거합니다. 초기 산스크리트어 문법 학자 Daz's는 상태, 예를 들어, 프라크리트 언어의 많은 어원 언어는 어원적으로 산스크리트어에 뿌리를두고 있지만, "문법의 무시"에서 발생하는 "소리의 손실"과 부패를 포함한다. 다우아린(Da)은 프라크리트에 산스크리트어와 는 별개로 번성하는 말과 혼란스러운 구조가 있다는 것을 인정했다. 이 견해는 고대 나야아스트라 텍스트의 저자인 바라타 무니의 글에서 찾을 수 있습니다. 초기 자인 학자 나미사두는 그 차이를 인정했지만, 프라크리트 어가 산스크리트어의 부패라고 는 데 동의하지 않았다. 나미사두는 프라크리트 어가 푸르바움(이전에 는 기원)이며 아이들에게 자연스럽게 다가왔으며, 산스크리트어는 "문법에 의한 정화"를 통해 프라크리트의 정제였다고 밝혔다. [45]
히스토리[편집]] [
원산지 및 개발[편집]] [
산스크리트어는 언어의 유도 유럽 가족에 속한다. 그것은 지금 프로토 - 인도 - 유럽언어라고 공통 루트 언어에서 발생 세 고대 문서화 언어 중 하나입니다 :[20][46][47]
- 베다 산스크리트어 (c. 1500 – 500 기원전).
- 미케네 그리스어 (기원전 1450년 경)[기원전 48년] 고대 그리스어(기원전 750년 – 기원전 400년). 미케네 그리스어는 그리스어의 가장 오래된 기록 된 형태이지만, 살아남은 제한된 재료는 매우 모호한 쓰기 시스템을가지고 있다. Indo-European 연구에 더 중요한 것은 고대 그리스어로, 두 개의 홈릭 시(일리아드와 오디세이,기원전 750년)로 시작하여 광범위하게 기록되었습니다.
- 히티트 (기원전 1750년 경 - 기원전 1200년). 이것은 올드 히트, 미들 히트인, 네오 히트틴으로 구별되는 모든 Indo-European 언어 중 가장 오래된 기록입니다. 그것은 초기 분리로 인해 가능성이 다른 사람과 차이가 있다. cuneiform 스크립트에서 중앙 터키의 점토 정제에서 발견, 그것은 다른 언어에서, 전혀, 단편적으로 만 발견 몇 가지 매우 오래된 기능을 가지고 있습니다. 그러나 동시에, 그것은 쓰기 시스템의 모호성과 함께 초기 음운 및 문법 변화의 큰 숫자를 겪은 것으로 보인다.
산스크리트어와 관련된 다른 Indo-유럽 언어는 고대와 고전 라틴어 (c. 600 BCE – 100 CE, 오래된 이탈리아어), 고딕 (고딕 언어,c. 350 CE), 올드 노르스 (c. 200 CE 및 이후), 올드 아베스타 (c. 후반 2 천년 BCE[49]및 젊은 Avestan (c. 2th 밀레니엄 BCE ]) 및 젊은 Avestan을 포함한다. [46][47] 인도-유럽 언어에서 베다산스크릿의 가장 가까운 고대 친척은 아프가니스탄 북동부와 히말라야 북서부의 외딴 힌두쿠시 지역에서 발견되는 누리스타어이며, [47][50] [51]뿐만 아니라 멸종된 아베스탄과 올드 페르시아어이다. [52][53][54] 산스크리트어는 유도-유럽 언어의 사템 그룹에 속한다.
라틴어와 그리스어에 익숙한 식민지 시대 학자들은 산스크리트어의 유사성에 충격을 받았다. 어휘와 문법 모두; 유럽의 고전 언어에. 【주 4】 그것은 세계의 주요 먼 고대 언어의 일부 사이의 공통의 루트와 역사적 링크를 제안했다. 윌리엄 존스는 이렇게 말했습니다.
산스크리트어는 고대가 무엇이든 훌륭한 구조입니다. 그리스어보다 더 완벽하고, 라틴어보다 더 풍성하고, 하나보다 더 정교하게 정제되었지만, 동사의 뿌리와 문법의 형태 모두에서 둘 다 더 강한 친화력을 지니고 있으며, 아마도 우연히 생산되었을 수 있는 것보다 더 강하다. 너무나 강해서, 어떤 철학자도 세 가지를 모두 조사할 수 없었고, 그들이 어떤 공통의 근원에서튀어나왔다고 믿지 않고는 더 이상 존재하지 않았을 것이다. 비슷한 이유가 있다, 비록 아주 그렇게 강제, 고 두와 셀틱 [sic], 비록 매우 다른 관용구와 혼합, 산스크리트어와 같은 기원을 했다; 그리고 올드 페르시아어는 같은 가족에 추가 될 수 있습니다.
— 윌리엄 존스, 1786년, 산스크리트어로토마스 버로우가인용함 [56]
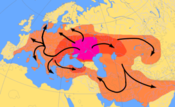
산스크리트어와 다른 인도-유럽 언어가 공유하는 일반적인 특징을 설명하기 위해 인도-아리아어 이주 이론에 따르면 산스크리트어가 된 최초의 연사들은 기원전 2차 기원전 초반에 북서쪽에서 인도 아대륙에 도착했다고 합니다. 이러한 이론에 대한 증거는 유도 - 이란어와 발트와 슬라브어 언어사이의 긴밀한 관계를 포함, 비 - 인도 - 유럽 우라어언어와 어휘 교환, 식물군과 동물 상에 대한 입증 된 Indo-European 단어의 본질. [57] 베다 산스크리트어를 선행 인도 아리아어 언어의 사전 역사는 불분명하고 다양한 가설은 상당히 넓은 한계를 통해 배치. 토마스 버로우에 따르면, 다양한 Indo-Europe 언어의 관계에 따라, 이 모든 언어의 기원은 아마도 현재 중부 또는 동부 유럽에있을 수 있습니다, 인도 - 이란 그룹은 아마도 중앙 러시아에서 발생하면서. [58] 이란과 인도-아리아인 지부는 아주 일찍 분리되었다. 기원전 2세기에 이란 동부와 남부로 이주한 인도-아리아 지부입니다. 고대 인도에 들어서자 인도-아리아어는 급속한 언어 적 변화를 겪었고 베다 산스크리트어로 변형되었습니다. [59]
베다 산스크리트어[편집]] [
산스크리트어의 사전 고전 형태는 베다 산스크리트어로알려져있다. 가장 일찍 증명된 산스크리트어 텍스트는 기원전 중반에서 후반까지 힌두교 성어인 리그베다(Rigveda)입니다. 그러한 초기 시대의 기록기록은 존재했다면 살아남지 못했다. 그러나 학자들은 텍스트의 구두 전송이 신뢰할 수 있다고 확신합니다 : 그들은 정확한 음성 표현과 보존이 역사적 전통의 일부였다 의식 문학이었다. [60][61][62]
리그베다(Rigveda)는 고대 인도의 먼 지역에서 온 여러 저자가 만든 책모음집입니다. 이 저자는 다른 세대를 대표하고, 만다라 2에서 7은 가장 오래된 반면 만다라 1과 10은 상대적으로 가장 젊은. [63][64] 그러나, 리그베다의 이 책에서 베다 산스크리트어는 "거의 어떤 변증적 다양성을 제시하지", 루이 르누말한다 - 특히 산스크리트어 문학과 리그베다의 그의 장학금으로 알려진 인학자. Renou에 따르면, 이것은 베다 산스크리트어가 기원전 2년 후반까지 "설정된 언어 적 패턴"을 가졌다는 것을 의미합니다. [65] 리그베다너머, 현대에 살아남은 베다 산스크리트어의 고대 문학으로는 브라마나스, 아라냐카, 초기 우파니샤드와같은 베다어집 텍스트와 함께 사아베베다, 야주르베다, 아타르바베다 등이 있다. [60] 이 베다 문서는 인도 북서부, 북부 및 동부 아대륙의 여러 지역에서 발견되는 산스크리트어방언을 반영한다. [8][66]
베다 산스크리트어는 고대 인도의 언어이자 문학언어였다. 마이클 비첼에 따르면, 베다 산스크리트어는 일시적으로 한 곳에 정착한 반 유목민 아리아의 언어였으며, 가축 떼를 유지하고, 제한된 농업을 실천했으며, 얼마 후 마차 열차로 옮겨진 그라마(grama)라고불렀다. [67][10] 베다 산스크리트어 또는 밀접하게 관련된 인도-유럽 변종은 고대 히티족과 미타니 족 사이의"미타니 조약"에 의해 입증된 바와 같이 고대 인도를 넘어 현재 시리아와 터키의 일부가 되는 지역에서 바위에 새겨진 것으로 인식되었다. [68][참고 5] 미타니 왕자의 이름과 말 훈련과 관련된 기술 용어와 같은이 조약의 일부는 이해하지 못하는 이유로 베다 산스크리트어의 초기 형태에 있습니다. 이 조약은 또한 베다 문학의 초기 층에서 발견 된 신 바루나, 미트라, 인드라와 나사티아를 호출합니다. [68][70]
O 브리하스파티, 이름을 줄 때
그들은 먼저 언어의 시작을 제시,
그들의 가장 우수하고 흠 없는 비밀
사랑을 통해 누워 있었다,
현명한 사람들이 마음으로 언어를 형성했을 때,
윈나우잉 팬과 곡물처럼 정화,
그런 다음 친구들은 우정을 알았습니다.
그들의 언어에 배치 상서로운 마크.
리그베다에서 발견되는 베다 산스크리트어는 다른 베다 문헌보다 훨씬 더 고풍스로, 여러 면에서 리그베다어는 올드 애베스타 조로아스터리안 가타스와 호머의 일리아드 와 오디세이의고풍스러운 글에서 발견되는 것과 특히 유사하다. [72] 스테파니 더블유 제이미슨과 조엘 P. 브레레튼에 따르면, 리그베다의번역으로 유명한 인학자인 인도-이란과 인도-유럽 시대에서 베다 산스크리트어 문학은 시인과 사제의 역할, 후원 경제, 관용구의 일부 와 같은 사회 구조에 대해 "분명히 물려받았다"고 한다. [73][참고 6] 유사점이 있지만, 상태 제이미슨과 브레튼, 베다 산스크리트어, 올드 아베스타, 미케네 그리스 문학 사이에도 차이가 있다. 예를 들어, 리그베다의산스크리트어 미소와는 달리, 올드 애베스타 가타스는 완전히 시밀리가 부족하며, 이후 버전에서는 드물게 사용된다. 리그베딕 산스크리트어와 같은 홈리안 그리스어는 시밀리를 광범위하게 배치하지만 구조적으로 매우 다릅니다. [75]
클래식 산스크리트어[편집]] [
산스크리트어의 초기 베다 형태는 훨씬 덜 균일했다, 그것은 더 구조화되고 균일 한 언어로 시간이 지남에 따라 진화, 궁극적으로 중반 1 천년 BCE에 의해 고전 산스크리트어로. 리처드 곰브리치에 따르면, 인디아학자이자 산스크리트어, 팔리, 불교학학자인 리그베다에서 발견된 고대 베다 산스크리트어는 베다 시대에 이미 진화했다고 한다. 힌두교의 초기 우파니샤드와 후기 베다 문학의 언어는 고전 산스크리트어에 접근, 부처님의시간에 의해 했던 고풍스러운 베다 산스크리트어는 고대 인도 현인을 제외한 모든 이해할 수 없게되는 동안, 곰브리히 상태. [76]
산스크리트어의 공식화는 파탄잘리의 마하바샤와 파탄잘리의 작품에 앞서 카티아야나의 해설과 함께 파나이니에기인한다. [77] 파니니는 아오하디야야("8장 문법")를 작곡했다. 그가 살았던 세기는 불분명하고 논쟁의 여지가 있지만, 그의 작품은 일반적으로 기원전 6 세기와 4 세기 사이에 언젠가 허용됩니다. [78][79][80]
아아드야야야는 산스크리트어 문법의 첫 번째 설명은 아니었지만, 전체적으로 살아남은 최초의 문법이다. 파우이니는 그 전에 산스크리트어 언어의 음운과 문법 적 측면에 10 학자뿐만 아니라 인도의 다른 지역에서 산스크리트어의 사용에 변형을 인용한다. [81] 그가 인용한 10명의 베다 학자들은 아피살리, 카시야파,가르야, 갈라바, 카크라바르마나, 바라드바자,사카타야나, 사칼리야, 세나카, 스포타야나이다. [82] 파니니의 아아하야야는 베당가인비야카라의 기초가 되었다. [83] 아오타히야야에서언어는 그리스어 나 라틴어 문법학자들 사이에 평행이 없는 방식으로 관찰된다. 레누와 필리오자트에 따르면 파우이니의 문법은 언어적 표현과 산스크리트어의 표준을 정한 고전을 정의한다. [84] 파우이니는 구문, 형태, 어휘로 구성된 기술적 메타어를 사용했다. 이 메타언어는 일련의 메타 규칙에 따라 구성되며, 그 중 일부는 명시적으로 명시되어 있으며 나머지는 추론할 수 있습니다. [85]
파우이니의 포괄적이고 과학적인 문법 이론은 전통적으로 고전 산스크리트어의 시작을 표시하기 위해 촬영됩니다. [86] 그의 체계적인 논문은 산스크리트어를 2천년 동안 배움과 문학의 탁월한 인도어로 만들었다. [87] 파우이니가 산스크리트어에 대한 논문을 썼는지, 구두로 구체적이고 정교한 논문을 작성한 다음 학생들을 통해 전달했는지는 불분명하다. 현대의 장학금은 일반적으로 그가 리피 ("스크립트") 및 리피카라 ("서기")와 같은 단어에 대한 참조에 따라 쓰기의 형태를 알고 있음을 받아 들인다 3.2 섹션의 A의 【88】[89][90][주 7]
파니니에 의해 공식화 고전 산스크리트어 언어, 르노는 "가난한 언어가 아니다", 오히려 "고고학과 불필요한 공식적인 대안이 배제된 제어 및 억제 언어"입니다. [97] 언어의 고전 형태는 산디 규칙을 단순화하지만, 엄격하고 유연성을 추가하면서, 베다어의 다양한 측면을 유지, 그래서 그것은 생각을 표현하는 충분한 수단을 가지고뿐만 아니라 "무한하게 다양한 문학의 미래 증가 요구에 응답 할 수있다", Renou에 따르면. 파니니는 베다 산스크리트어의 바울람 틀을 넘어서는 수많은 "선택적 규칙"을 포함시켰으며, 자유와 창의성을 존중하여 지리나 시간으로 구분된 개별 작가들이 산스크리트어의 경쟁적인 형태를 따르는 자신만의 방식으로 사실과 견해를 표현할 수 있는 선택권을 갖게 되었다. [98]
인도-아리아어와 베다 산스크리트어 사이의 베다 이전 기간에 발생해야 하는 강렬한 변화에 비해 베다 산스크리트어와 클래식 산스크리트어 사이의 발음 차이는 무시할 수 있습니다. [99] 베다와 고전 산스크리트어 사이의 눈에 띄는 차이점은 악센트, 의미론과 구문의 차이뿐만 아니라 많이 확장 된 문법과 문법 범주를 포함한다. [100] 명사와 동사 중 일부가 끝나는 방법과 내부 및 외부 모두의 샌드피 규칙 사이에는 몇 가지 차이점이 있습니다. [100] 초기 베다 산스크리트어 언어에서 발견 된 꽤 많은 단어는 후반 베다 산스크리트어 또는 고전 산스크리트어 문학에서 발견되지 않습니다, 일부 단어는 문맥적으로 초기 베다 산스크리트어 문학에 비해 때 고전 산스크리트어에서 다른 새로운 의미를 가지고있는 동안. 【100】
아서 마도네렐은 베다와 고전 산스크리트어 사이의 차이점중 일부를 요약 초기 식민지 시대 학자 중 하나였다. [100][101] 루이 르노는 1956년에 프랑스어로 베다 시대의 베다 산스크리트어의 유사점, 차이점 및 진화에 대한 보다 광범위한 논의를 거쳐 역사에 대한 그의 견해와 함께 고전 산스크리트어에 발표했다. 이 작품은 재반스 발비르에 의해 번역되었습니다. [102]
산스크리트어 및 프라크리트 어[편집]] [

야쇼드하만-비슈누바르다나, 532 CE의 만사우르스 돌 비문. [103]
단어 Sa우스크치타 (산스크리트어)의 초기 알려진 사용, 언어의 맥락에서, 절에서 발견된다 3.16.14 과 5.28.17-19 라마야나. 【 104 】【 주 8 】 고전 산스크리트어의 배운 영역 외부, 언어 구어체 방언(Prakrits)진화를 계속했다. 산스크리트어는 고대 인도의 수많은 다른 프라크리트 언어와 공존했다. 인도의 프라크리트 언어는 또한 고대의 뿌리를 가지고 있으며, 일부 산스크리트어 학자들은 말 그대로 "버릇"이 아파브람사라고했다. [106][107] 베다 문학은 다른 인도-유럽 언어에서 찾을 수 없지만 지역 프라크리트 어에서 발견되는 음성 동등한 단어를 포함하고 있으며, 이는 인도 역사의 초기에 단어와 아이디어의 상호 작용, 공유가 시작된 것으로 보인다. 인도인들이 힌두교의 초기 신념, 특히 불교와 자이니즘의형태로 도전하면서, 테라바다 불교의 팔리와 자이니즘의 아르하마가디와 같은 프라크리트 어는 고대에 산스크리트어와 경쟁했다. [108][109][110] 그러나, 폴 던다스,자이니즘의 학자, 이 고대 프라크리트 언어는 "라틴어에 중세 이탈리아와 거의 같은 관계를 가지고 있다." [110] 인도 전통에 따르면 부처와 마하비라는 모든 사람이 이해할 수 있도록 프라크리트 어를 선호했다. 그러나 던다스와 같은 학자들은 이 가설에 의문을 제기했다. 그들은 이것에 대한 증거가 없으며 어떤 증거가 가능한지 공통 시대의 시작으로 배운 승려 이외의 다른 사람은 아르다마가디와같은 오래된 프라크리트 언어를 이해할 수있는 능력이 거의 없다는 것을 시사합니다. 【110】[주9]
식민지 시대의 학자들은 산스크리트어가 이제까지 말한 언어인지 아니면 단지 문학언어인지 에 대해 의문을 제기했다. [112] 학자들은 그들의 대답에 동의하지 않는다. 서양 학자들의 한 섹션은 산스크리트어가 결코 말한 언어가 아니었다고 말하는 반면, 다른 학자들과 특히 대부분의 인도 학자들은 그 반대의 입장을 밝혔다. [113] 산스크리트어를 긍정하는 사람들은 고대 인도에서 산스크리트어 원고의 광대 한 수를 보존 구전 전통에 대한 음성 언어인 산스크리트어의 필요성에 대한 언어 포인트되었습니다. 둘째, 그들은 야크사, 파니니, 파타나잘리의 작품에서 텍스트 증거가 그 시대의 고전 산스크리트어가 문화와 교육에 의해사용되는언어라고 단언한다고 명시합니다. 일부 sutras 는 기록 된 산스크리트어 대 음성 산스크리트어의 변형 형태에 대해 해설. [113] 7세기 중국 불교 순례자 쉬안장은 그의 회고록에서 인도의 공식 철학적 토론이 그 지역의 언어가 아니라 산스크리트어에서 열렸다고 언급했다. [113]
산스크리트어 언어학자 인 Madhav Deshpande에따르면, 산스크리트어는 문학 산스크리트어의 보다 공식적이고 문법적으로 올바른 형태와 공존하는 1세기 중반 BCE의 구어체 형태로 사용되는 언어였습니다. [12] Deshpande는 언어의 구어체부정확한 근사치와 방언이 말하고 이해되는 현대 언어와 문학 작품에서 발견되는 동일한 언어의 "세련되고 정교하며 문법적으로 정확한" 형태에 대해 사실이라고 말합니다. [12] 인도의 전통, 말 모리스 Winternitz,학습과 고대에서 여러 언어의 사용을 선호하고있다. 산스크리트어는 교육받은 엘리트 계급에서 사용되는 언어였지만, 라마야나, 마하바라타, 바가바타 푸라나, 판차탄트라 및 기타 많은 텍스트가 모두 산스크리트어에 있기 때문에 사회의 더 넓은 서클에서 이해되어야 하는 언어이기도 합니다. [114] 정확한 문법을 가진 고전 산스크리트어는 따라서 인도 학자들과 교육받은 계급의 언어였고, 다른 사람들은 그 언어의 대략적인 또는 비문법적 변형과 다른 자연 인도 언어와 통신했다. [12] 산스크리트어, 고대 인도의 배운 언어로, 따라서 언어 Prakrits와 함께 존재. [12] 많은 산스크리트어 드라마는 언어가 언어 Prakrits와 공존했음을 나타냅니다. 바라나시, 파이탄, 푸네, 칸치푸람의 센터는 식민지 시대가 도래할 때까지 고전 산스크리트어 학습과 공개 토론의 중심지였다. [115]
에티엔 라모테(Étienne Lamotte)에따르면, 인학자이자 불교 학자인 산스크리트어는 의사소통의 정확성 때문에 지배적인 문학및 비문언어가 되었다. 그것은, 상태 Lamotte, 아이디어를 제시하기위한 이상적인 악기와 산스크리트어에 대한 지식은 그렇게 확산과 영향력을 했다 곱했다. [116] 산스크리트어는 높은 문화, 예술, 심오한 아이디어의 수단으로 자발적으로 채택되었다. 폴락은 라모테에 동의하지 않지만, 산스크리트어의 영향력은 그가 남아시아와 동남 아시아의 대부분을 포함하는 지역을 통해 "산스크리트어 코스모폴리스"로 용어로 성장한 것을 동의합니다. 산스크리트어 국제정신은 인도를 넘어 300년에서 1300년 사이에 번성했다. [117]
Influence[edit]
— Foreword of Sanskrit Computational Linguistics (2009), Gérard Huet, Amba Kulkarni and Peter Scharf[118][119][note 10]
Sanskrit has been the predominant language of Hindu texts encompassing a rich tradition of philosophical and religious texts, as well as poetry, music, drama, scientific, technical and others.[121][122] It is the predominant language of one of the largest collection of historic manuscripts. The earliest known inscriptions in Sanskrit are from the 1st century BCE, such as the Ayodhya Inscription of Dhana and Ghosundi-Hathibada (Chittorgarh).[30]
Though developed and nurtured by scholars of orthodox schools of Hinduism, Sanskrit has been the language for some of the key literary works and theology of heterodox schools of Indian philosophies such as Buddhism and Jainism.[123][124] The structure and capabilities of the Classical Sanskrit language launched ancient Indian speculations about "the nature and function of language", what is the relationship between words and their meanings in the context of a community of speakers, whether this relationship is objective or subjective, discovered or is created, how individuals learn and relate to the world around them through language, and about the limits of language?[123][125] They speculated on the role of language, the ontological status of painting word-images through sound, and the need for rules so that it can serve as a means for a community of speakers, separated by geography or time, to share and understand profound ideas from each other.[125][note 11] These speculations became particularly important to the Mimamsa and the Nyaya schools of Hindu philosophy, and later to Vedanta and Mahayana Buddhism, states Frits Staal—a scholar of Linguistics with a focus on Indian philosophies and Sanskrit.[123] Though written in a number of different scripts, the dominant language of Hindu texts has been Sanskrit. It or a hybrid form of Sanskrit became the preferred language of Mahayana Buddhism scholarship.[128] one of the early and influential Buddhist philosopher Nagarjuna (~200 CE), for example, used Classical Sanskrit as the language for his texts.[129] According to Renou, Sanskrit had a limited role in the Theravada tradition (formerly known as the Hinayana) but the Prakrit works that have survived are of doubtful authenticity. Some of the canonical fragments of the early Buddhist traditions, discovered in the 20th century, suggest the early Buddhist traditions used an imperfect and reasonably good Sanskrit, sometimes with a Pali syntax, states Renou. The Mahāsāṃghika and Mahavastu, in their late Hinayana forms, used hybrid Sanskrit for their literature.[130] Sanskrit was also the language of some of the oldest surviving, authoritative and much followed philosophical works of Jainism such as the Tattvartha Sutra by Umaswati.[131][132]

The Sanskrit language has been one of the major means for the transmission of knowledge and ideas in Asian history. Indian texts in Sanskrit were already in China by 402 CE, carried by the influential Buddhist pilgrim Faxian who translated them into Chinese by 418 CE.[136] Xuanzang, another Chinese Buddhist pilgrim, learnt Sanskrit in India and carried 657 Sanskrit texts to China in the 7th century where he established a major center of learning and language translation under the patronage of Emperor Taizong.[137][138] By the early 1st millennium CE, Sanskrit had spread Buddhist and Hindu ideas to Southeast Asia,[14] parts of the East Asia[15] and the Central Asia.[16] It was accepted as a language of high culture and the preferred language by some of the local ruling elites in these regions.[139] According to the Dalai Lama, the Sanskrit language is a parent language that is at the foundation of many modern languages of India and the one that promoted Indian thought to other distant countries. In Tibetan Buddhism, states the Dalai Lama, Sanskrit language has been a revered one and called legjar lhai-ka or "elegant language of the gods". It has been the means of transmitting the "profound wisdom of Buddhist philosophy" to Tibet.[140]

The Sanskrit language created a pan-Indic accessibility to information and knowledge in the ancient and medieval times, in contrast to the Prakrit languages which were understood just regionally.[115][143] It created a cultural bond across the subcontinent.[143] As local languages and dialects evolved and diversified, Sanskrit served as the common language.[143] It connected scholars from distant parts of the Indian subcontinent such as Tamil Nadu and Kashmir, states Deshpande, as well as those from different fields of studies, though there must have been differences in its pronunciation given the first language of the respective speakers. The Sanskrit language brought Indic people together, particularly its elite scholars.[115] Some of these scholars of Indian history regionally produced vernacularized Sanskrit to reach wider audiences, as evidenced by texts discovered in Rajasthan, Gujarat, and Maharashtra. once the audience became familiar with the easier to understand vernacularized version of Sanskrit, those interested could graduate from colloquial Sanskrit to the more advanced Classical Sanskrit. Rituals and the rites-of-passage ceremonies have been and continue to be the other occasions where a wide spectrum of people hear Sanskrit, and occasionally join in to speak some Sanskrit words such as "namah".[115]
Classical Sanskrit is the standard register as laid out in the grammar of Pāṇini, around the fourth century BCE.[144] Its position in the cultures of Greater India is akin to that of Latin and Ancient Greek in Europe. Sanskrit has significantly influenced most modern languages of the Indian subcontinent, particularly the languages of the northern, western, central and eastern Indian subcontinent.[25][26][27]
Decline[edit]
Sanskrit declined starting about and after the 13th century.[117][145] This coincides with the beginning of Islamic invasions of the Indian subcontinent to create, thereafter expand the Muslim rule in the form of Sultanates and later the Mughal Empire.[146] With the fall of Kashmir around the 13th century, a premier center of Sanskrit literary creativity, Sanskrit literature there disappeared,[147] perhaps in the "fires that periodically engulfed the capital of Kashmir" or the "Mongol invasion of 1320" states Sheldon Pollock.[148]:397–398 The Sanskrit literature which was once widely disseminated out of the northwest regions of the subcontinent, stopped after the 12th century.[148]:398 As Hindu kingdoms fell in the eastern and the South India, such as the great Vijayanagara Empire, so did Sanskrit.[147] There were exceptions and short periods of imperial support for Sanskrit, mostly concentrated during the reign of the tolerant Mughal emperor Akbar.[149] Muslim rulers patronized the Middle Eastern language and scripts found in Persia and Arabia, and the Indians linguistically adapted to this Persianization to gain employment with the Muslim rulers.[150] Hindu rulers such as Shivaji of the Maratha Empire, reversed the process, by re-adopting Sanskrit and re-asserting their socio-linguistic identity.[150][151][152] After Islamic rule disintegrated in the Indian subcontinent and the colonial rule era began, Sanskrit re-emerged but in the form of a "ghostly existence" in regions such as Bengal. This decline was the result of "political institutions and civic ethos" that did not support the historic Sanskrit literary culture.[147]
Scholars are divided on whether or when Sanskrit died. Western authors such as John Snelling state that Sanskrit and Pali are both dead Indian languages.[153] Indian authors such as M Ramakrishnan Nair state that Sanskrit was a dead language by the 1st millennium BCE.[154] Sheldon Pollock states that in some crucial way, "Sanskrit is dead".[148]:393 After the 12th century, the Sanskrit literary works were reduced to "reinscription and restatements" of ideas already explored, and any creativity was restricted to hymns and verses. This contrasted with the previous 1,500 years when "great experiments in moral and aesthetic imagination" marked the Indian scholarship using Classical Sanskrit, states Pollock.[148]:398
Other scholars state that Sanskrit language did not die, only declined. Hanneder disagrees with Pollock, finding his arguments elegant but "often arbitrary". According to Hanneder, a decline or regional absence of creative and innovative literature constitutes a negative evidence to Pollock's hypothesis, but it is not positive evidence. A closer look at Sanskrit in the Indian history after the 12th century suggests that Sanskrit survived despite the odds. According to Hanneder,[155]
On a more public level the statement that Sanskrit is a dead language is misleading, for Sanskrit is quite obviously not as dead as other dead languages and the fact that it is spoken, written and read will probably convince most people that it cannot be a dead language in the most common usage of the term. Pollock's notion of the "death of Sanskrit" remains in this unclear realm between academia and public opinion when he says that "most observers would agree that, in some crucial way, Sanskrit is dead."[147]
The Sanskrit language scholar Moriz Winternitz states, Sanskrit was never a dead language and it is still alive though its prevalence is lesser than ancient and medieval times. Sanskrit remains an integral part of Hindu journals, festivals, Ramlila plays, drama, rituals and the rites-of-passage.[156] Similarly, Brian Hatcher states that the "metaphors of historical rupture" by Pollock are not valid, that there is ample proof that Sanskrit was very much alive in the narrow confines of surviving Hindu kingdoms between the 13th and 18th centuries, and its reverence and tradition continues.[157]
Hanneder states that modern works in Sanskrit are either ignored or their "modernity" contested.[158]
According to Robert Goldman and Sally Sutherland, Sanskrit is neither "dead" nor "living" in the conventional sense. It is a special, timeless language that lives in the numerous manuscripts, daily chants and ceremonial recitations, a heritage language that Indians contextually prize and some practice.[159]
When the British introduced English to India in the 19th century, knowledge of Sanskrit and ancient literature continued to flourish as the study of Sanskrit changed from a more traditional style into a form of analytical and comparative scholarship mirroring that of Europe.[160]
Modern Indic languages[edit]
The relationship of Sanskrit to the Prakrit languages, particularly the modern form of Indian languages, is complex and spans about 3,500 years, states Colin Masica—a linguist specializing in South Asian languages. A part of the difficulty is the lack of sufficient textual, archaeological and epigraphical evidence for the ancient Prakrit languages with rare exceptions such as Pali, leading to a tendency of anachronistic errors.[161] Sanskrit and Prakrit languages may be divided into Old Indo-Aryan (1500 BCE–600 BCE), Middle Indo-Aryan (600 BCE–1000 CE) and New Indo-Aryan (1000 CE–current), each can further be subdivided in early, middle or second, and late evolutionary substages.[161]
Vedic Sanskrit belongs to the early Old Indo-Aryan while Classical Sanskrit to the later Old Indo-Aryan stage. The evidence for Prakrits such as Pali (Theravada Buddhism) and Ardhamagadhi (Jainism), along with Magadhi, Maharashtri, Sinhala, Sauraseni and Niya (Gandhari), emerge in the Middle Indo-Aryan stage in two versions—archaic and more formalized—that may be placed in early and middle substages of the 600 BCE–1000 CE period.[161] Two literary Indic languages can be traced to the late Middle Indo-Aryan stage and these are Apabhramsa and Elu (a form of literary Sinhalese). Numerous North, Central, Eastern and Western Indian languages, such as Hindi, Gujarati, Sindhi, Punjabi, Kashmiri, Nepali, Braj, Awadhi, Bengali, Assamese, Oriya, Marathi, and others belong to the New Indo-Aryan stage.[161]
There is an extensive overlap in the vocabulary, phonetics and other aspects of these New Indo-Aryan languages with Sanskrit, but it is neither universal nor identical across the languages. They likely emerged from a synthesis of the ancient Sanskrit language traditions and an admixture of various regional dialects. Each language has some unique and regionally creative aspects, with unclear origins. Prakrit languages do have a grammatical structure, but like the Vedic Sanskrit, it is far less rigorous than Classical Sanskrit. The roots of all Prakrit languages may be in the Vedic Sanskrit and ultimately the Indo-Aryan language, their structural details vary from the Classical Sanskrit.[24][161] It is generally accepted by scholars and widely believed in India that the modern Indic languages, such as Bengali, Gujarati, Hindi and Punjabi are descendants of the Sanskrit language.[162][163][164] Sanskrit, states Burjor Avari, can be described as "the mother language of almost all the languages of north India".[165]
Geographic distribution[edit]
The Sanskrit language's historic presence is attested across a wide geography beyond the Indian subcontinent. Inscriptions and literary evidence suggests that Sanskrit language was already being adopted in Southeast Asia and Central Asia in the 1st millennium CE, through monks, religious pilgrims and merchants.[166][167][168]
The Indian subcontinent has been the geographic range of the largest collection of the ancient and pre-18th-century Sanskrit manuscripts and inscriptions.[120] Beyond ancient India, significant collections of Sanskrit manuscripts and inscriptions have been found in China (particularly the Tibetan monasteries),[169][170] Myanmar,[171] Indonesia,[172] Cambodia,[173] Laos,[174] Vietnam,[175] Thailand,[176] and Malaysia.[174] Sanskrit inscriptions, manuscripts or its remnants, including some of the oldest known Sanskrit written texts, have been discovered in dry high deserts and mountainous terrains such as in Nepal,[177][178][note 12] Tibet,[170][179] Afghanistan,[180][181] Mongolia,[182] Uzbekistan,[183] Turkmenistan, Tajikistan,[183] and Kazakhstan.[184] Some Sanskrit texts and inscriptions have also been discovered in Korea and Japan.[185][186][187]
Official status[edit]
In India, Sanskrit is among the 22 official languages of India in the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution.[188] In 2010, Uttarakhand became the first state in India to make Sanskrit its second official language.[189] In 2019, Himachal Pradesh made Sanskrit its second official language, becoming the second state in India to do so.[190]
Phonology[edit]
Sanskrit shares many Proto-Indo-European phonological features, although it features a larger inventory of distinct phonemes. The consonantal system is the same, though it systematically enlarged the inventory of distinct sounds. For example, Sanskrit added a voiceless aspirated "tʰ", to the voiceless "t", voiced "d" and voiced aspirated "dʰ" found in PIE languages.[191]
The most significant and distinctive phonological development in Sanskrit is vowel-merger, states Stephanie Jamison—an Indo-European linguist specializing in Sanskrit literature.[191] The short *e, *o and *a, all merge as a (अ) in Sanskrit, while long *ē, *ō and *ā, all merge as long ā (आ). These mergers occurred very early and significantly impacted Sanskrit's morphological system.[191] Some phonological developments in it mirror those in other PIE languages. For example, the labiovelars merged with the plain velars as in other satem languages. The secondary palatalization of the resulting segments is more thorough and systematic within Sanskrit, states Jamison.[191] A series of retroflex dental stops were innovated in Sanskrit to more thoroughly articulate sounds for clarity. For example, unlike the loss of the morphological clarity from vowel contraction that is found in early Greek and related southeast European languages, Sanskrit deployed *y, *w, and *s intervocalically to provide morphological clarity.[191]
Vowels[edit]
The cardinal vowels (svaras) i (इ), u (उ), a (अ) distinguish length in Sanskrit, states Jamison.[192][193] The short a (अ) in Sanskrit is a closer vowel than ā, equivalent to schwa. The mid-vowels ē (ए) and ō (ओ) in Sanskrit are monophthongizations of the Indo-Iranian diphthongs *ai and *au. The Old Iranian language preserved *ai and *au.[192] The Sanskrit vowels are inherently long, though often transcribed e and o without the diacritic. The vocalic liquid r̥ in Sanskrit is a merger of PIE *r̥ and *l̥. The long r̥ is an innovation and it is used in a few analogically generated morphological categories.[192][194][195]
| Independent form | IAST/ ISO | Independent form | IAST/ ISO | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| kaṇṭhya (Guttural) | अ | a | आ | ā | ||
| tālavya (Palatal) | इ | i | ई | ī | ||
| oṣṭhya (Labial) | उ | u | ऊ | ū | ||
| mūrdhanya (Retroflex) | ऋ | ṛ/r̥ | ॠ | ṝ/r̥̄ | ||
| dantya (Dental) | ऌ | ḷ/l̥ | (ॡ) | (ḹ/l̥̄)[197] | ||
| kaṇṭhatālavya (Palatoguttural) | ए | e/ē | ऐ | ai | ||
| kaṇṭhoṣṭhya (Labioguttural) | ओ | o/ō | औ | au | ||
| (consonantal allophones) | अं | aṃ/aṁ[198] | अः | aḥ[199] |
According to Masica, Sanskrit has four traditional semivowels, with which were classed, "for morphophonemic reasons, the liquids: y, r, l, and v; that is, as y and v were the non-syllabics corresponding to i, u, so were r, l in relation to r̥ and l̥".[200] The northwestern, the central and the eastern Sanskrit dialects have had a historic confusion between "r" and "l". The Paninian system that followed the central dialect preserved the distinction, likely out of reverence for the Vedic Sanskrit that distinguished the "r" and "l". However, the northwestern dialect only had "r", while the eastern dialect probably only had "l", states Masica. Thus literary works from different parts of ancient India appear inconsistent in their use of "r" and "l", resulting in doublets that is occasionally semantically differentiated.[200]
Consonants[edit]
Sanskrit possesses a symmetric consonantal phoneme structure based on how the sound is articulated, though the actual usage of these sounds conceals the lack of parallelism in the apparent symmetry possibly from historical changes within the language.[201]
| sparśa (Plosive) | anunāsika (Nasal) | antastha (Approximant) | ūṣman/saṃgharṣhī (Fricative) | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voicing → | aghoṣa | ghoṣa | aghoṣa | ||||||||||||||||||
| Aspiration → | alpaprāṇa | mahāprāṇa | alpaprāṇa | mahāprāṇa | alpaprāṇa | mahāprāṇa | |||||||||||||||
| kaṇṭhya (Guttural) | क | ka | /k/ | ख | kha | /kʰ/ | ग | ga | /g/ | घ | gha | /gʱ/ | ङ | ṅa | /ŋ/ | ह | ha | /ɦ/ | |||
| tālavya (Palatal) | च | ca | /c/ /t͡ɕ/ | छ | cha | /cʰ/ /t͡ɕʰ/ | ज | ja | /ɟ/ /d͡ʑ/ | झ | jha | /ɟʱ/ /d͡ʑʱ/ | ञ | ña | /ɲ/ | य | ya | /j/ | श | śa | /ɕ/ |
| mūrdhanya (Retroflex) | ट | ṭa | /ʈ/ | ठ | ṭha | /ʈʰ/ | ड | ḍa | /ɖ/ | ढ | ḍha | /ɖʱ/ | ण | ṇa | /ɳ/ | र | ra | /ɽ/ | ष | ṣa | /ʂ/ |
| dantya (Dental) | त | ta | /t/ | थ | tha | /tʰ/ | द | da | /d/ | ध | dha | /dʱ/ | न | na | /n/ | ल | la | /l/ | स | sa | /s/ |
| oṣṭhya (Labial) | प | pa | /p/ | फ | pha | /pʰ/ | ब | ba | /b/ | भ | bha | /bʱ/ | म | ma | /m/ | व | va | /ʋ/ | |||
Sanskrit had a series of retroflex stops. All the retroflexes in Sanskrit are in "origin conditioned alternants of dentals, though from the beginning of the language they have a qualified independence", states Jamison.[201]
Regarding the palatal plosives, the pronunciation is a matter of debate. In contemporary attestation, the palatal plosives are a regular series of palatal stops, supported by most Sanskrit sandhi rules. However, the reflexes in descendant languages, as well as a few of the sandhi rules regarding ch, could suggest an affricate pronunciation.
jh was a marginal phoneme in Sanskrit, hence its phonology is more difficult to reconstruct; it was more commonly employed in the Middle Indo-Aryan languages as a result of phonological processes resulting in the phoneme.
The palatal nasal is a conditioned variant of n occurring next to palatal obstruents.[201] The anusvara that Sanskrit deploys is a conditioned alternant of postvocalic nasals, under certain sandhi conditions.[202] Its visarga is a word-final or morpheme-final conditioned alternant of s and r under certain sandhi conditions.[202]
[The] order of Sanskrit sounds works along three principles: it goes from simple to complex; it goes from the back to the front of the mouth; and it groups similar sounds together. [...] Among themselves, both the vowels and consonants are ordered according to where in the mouth they are pronounced, going from back to front.
— A. M. Ruppel, The Cambridge Introduction to Sanskrit[203]
The voiceless aspirated series is also an innovation in Sanskrit but is significantly rarer than the other three series.[201]
While the Sanskrit language organizes sounds for expression beyond those found in the PIE language, it retained many features found in the Iranian and Balto-Slavic languages. An example of a similar process in all three, states Jamison, is the retroflex sibilant ʂ being the automatic product of dental s following i, u, r, and k (mnemonically "ruki").[202]
Phonological alternations, sandhi rules[edit]
Sanskrit deploys extensive phonological alternations on different linguistic levels through sandhi rules (literally, the rules of "putting together, union, connection, alliance"). This is similar to the English alteration of "going to" as gonna, states Jamison.[204] The Sanskrit language accepts such alterations within it, but offers formal rules for the sandhi of any two words next to each other in the same sentence or linking two sentences. The external sandhi rules state that similar short vowels coalesce into a single long vowel, while dissimilar vowels form glides or undergo diphthongization.[204] Among the consonants, most external sandhi rules recommend regressive assimilation for clarity when they are voiced. According to Jamison, these rules ordinarily apply at compound seams and morpheme boundaries.[204] In Vedic Sanskrit, the external sandhi rules are more variable than in Classical Sanskrit.[205]
The internal sandhi rules are more intricate and account for the root and the canonical structure of the Sanskrit word. These rules anticipate what are now known as the Bartholomae's law and Grassmann's law. For example, states Jamison, the "voiceless, voiced, and voiced aspirated obstruents of a positional series regularly alternate with each other (p ≈ b ≈ bʰ; t ≈ d ≈ dʰ, etc.; note, however, c ≈ j ≈ h), such that, for example, a morpheme with an underlying voiced aspirate final may show alternants[clarification needed] with all three stops under differing internal sandhi conditions".[206] The velar series (k, g, gʰ) alternate with the palatal series (c, j, h), while the structural position of the palatal series is modified into a retroflex cluster when followed by dental. This rule create two morphophonemically distinct series from a single palatal series.[206]
Vocalic alternations in the Sanskrit morphological system is termed "strengthening", and called guna and vriddhi in the preconsonantal versions. There is an equivalence to terms deployed in Indo-European descriptive grammars, wherein Sanskrit's unstrengthened state is same as the zero-grade, guna corresponds to normal-grade, while vriddhi is same as the lengthened-state.[207] The qualitative ablaut is not found in Sanskrit just like it is absent in Iranian, but Sanskrit retains quantitative ablaut through vowel strengthening.[207] The transformations between unstrengthened to guna is prominent in the morphological system, states Jamison, while vriddhi is a particularly significant rule when adjectives of origin and appurtenance are derived. The manner in which this is done slightly differs between the Vedic and the Classical Sanskrit.[207][208]
Sanskrit grants a very flexible syllable structure, where they may begin or end with vowels, be single consonants or clusters. Similarly, the syllable may have an internal vowel of any weight. The Vedic Sanskrit shows traces of following the Sievers-Edgerton Law, but Classical Sanskrit doesn't. Vedic Sanskrit has a pitch accent system, states Jamison, which were acknowledged by Panini, but in his Classical Sanskrit the accents disappear.[209] Most Vedic Sanskrit words have one accent. However, this accent is not phonologically predictable, states Jamison.[209] It can fall anywhere in the word and its position often conveys morphological and syntactic information.[209] According to Masica, the presence of an accent system in Vedic Sanskrit is evidenced from the markings in the Vedic texts. This is important because of Sanskrit's connection to the PIE languages and comparative Indo-European linguistics.[210]
Sanskrit, like most early Indo-European languages, lost the so-called "laryngeal consonants (cover-symbol *H) present in the Proto-Indo-European", states Jamison.[209] This significantly impacted the evolutionary path of the Sanskrit phonology and morphology, particularly in the variant forms of roots.[211]
Morphology[edit]
The basis of Sanskrit morphology is the root, states Jamison, "a morpheme bearing lexical meaning".[212] The verbal and nominal stems of Sanskrit words are derived from this root through the phonological vowel-gradation processes, the addition of affixes, verbal and nominal stems. It then adds an ending to establish the grammatical and syntactic identity of the stem. According to Jamison, the "three major formal elements of the morphology are (i) root, (ii) affix, and (iii) ending; and they are roughly responsible for (i) lexical meaning, (ii) derivation, and (iii) inflection respectively".[213]
A Sanskrit word has the following canonical structure:[212]
- Root + Affix
0-n + Ending
0–1
The root structure has certain phonological constraints. Two of the most important constraints of a "root" is that it does not end in a short "a" (अ) and that it is monosyllabic.[212] In contrast, the affixes and endings commonly do. The affixes in Sanskrit are almost always suffixes, with exceptions such as the augment "a-" added as prefix to past tense verb forms and the "-na/n-" infix in single verbal present class, states Jamison.[212]
A verb in Sanskrit has the following canonical structure:[214]
- Root + Suffix
Tense-Aspect + Suffix
Mood + Ending
Personal-Number-Voice
According to Ruppel, verbs in Sanskrit express the same information as other Indo-European languages such as English.[215] Sanskrit verbs describe an action or occurrence or state, its embedded morphology informs as to "who is doing it" (person or persons), "when it is done" (tense) and "how it is done" (mood, voice). The Indo-European languages differ in the detail. For example, the Sanskrit language attaches the affixes and ending to the verb root, while the English language adds small independent words before the verb. In Sanskrit, these elements co-exist within the word.[215][note 15]
| Sanskrit word equivalent | ||
|---|---|---|
| English expression | IAST/ISO | Devanagari |
| you carry | bharasi | भरसि |
| they carry | bharanti | भरन्ति |
| you will carry | bhariṣyasi | भरिष्यसि |
Both verbs and nouns in Sanskrit are either thematic or athematic, states Jamison.[217] Guna (strengthened) forms in the active singular regularly alternate in athematic verbs. The finite verbs of Classical Sanskrit have the following grammatical categories: person, number, voice, tense-aspect, and mood. According to Jamison, a portmanteau morpheme generally expresses the person-number-voice in Sanskrit, and sometimes also the ending or only the ending. The mood of the word is embedded in the affix.[217]
These elements of word architecture are the typical building blocks in Classical Sanskrit, but in Vedic Sanskrit these elements fluctuate and are unclear. For example, in the Rigveda preverbs regularly occur in tmesis, states Jamison, which means they are "separated from the finite verb".[212] This indecisiveness is likely linked to Vedic Sanskrit's attempt to incorporate accent. With nonfinite forms of the verb and with nominal derivatives thereof, states Jamison, "preverbs show much clearer univerbation in Vedic, both by position and by accent, and by Classical Sanskrit, tmesis is no longer possible even with finite forms".[212]
While roots are typical in Sanskrit, some words do not follow the canonical structure.[213] A few forms lack both inflection and root. Many words are inflected (and can enter into derivation) but lack a recognizable root. Examples from the basic vocabulary include kinship terms such as mātar- (mother), nas- (nose), śvan- (dog). According to Jamison, pronouns and some words outside the semantic categories also lack roots, as do the numerals. Similarly, the Sanskrit language is flexible enough to not mandate inflection.[213]
The Sanskrit words can contain more than one affix that interact with each other. Affixes in Sanskrit can be athematic as well as thematic, according to Jamison.[218] Athematic affixes can be alternating. Sanskrit deploys eight cases, namely nominative, accusative, instrumental, dative, ablative, genitive, locative, vocative.[218]
Stems, that is "root + affix", appear in two categories in Sanskrit: vowel stems and consonant stems. Unlike some Indo-European languages such as Latin or Greek, according to Jamison, "Sanskrit has no closed set of conventionally denoted noun declensions". Sanskrit includes a fairly large set of stem-types.[219] The linguistic interaction of the roots, the phonological segments, lexical items and the grammar for the Classical Sanskrit consist of four Paninian components. These, states Paul Kiparsky, are the Astadhyaayi, a comprehensive system of 4,000 grammatical rules, of which a small set are frequently used; Sivasutras, an inventory of anubandhas (markers) that partition phonological segments for efficient abbreviations through the pratyharas technique; Dhatupatha, a list of 2,000 verbal roots classified by their morphology and syntactic properties using diacritic markers, a structure that guides its writing systems; and, the Ganapatha, an inventory of word groups, classes of lexical systems.[220] There are peripheral adjuncts to these four, such as the Unadisutras, which focus on irregularly formed derivatives from the roots.[220]
Sanskrit morphology is generally studied in two broad fundamental categories: the nominal forms and the verbal forms. These differ in the types of endings and what these endings mark in the grammatical context.[213] Pronouns and nouns share the same grammatical categories, though they may differ in inflection. Verb-based adjectives and participles are not formally distinct from nouns. Adverbs are typically frozen case forms of adjectives, states Jamison, and "nonfinite verbal forms such as infinitives and gerunds also clearly show frozen nominal case endings".[213]
Tense and voice[edit]
The Sanskrit language includes five tenses: present, future, past imperfect, past aorist and past perfect.[216] It outlines three types of voices: active, passive and the middle.[216] The middle is also referred to as the mediopassive, or more formally in Sanskrit as parasmaipada (word for another) and atmanepada (word for oneself).[214]
| Active | Middle (Mediopassive) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Person | Singular | Dual | Plural | Singular | Dual | Plural |
| 1st | -mi | -vas | -mas | -e | -vahe | -mahe |
| 2nd | -si | -thas | -tha | -se | -āthe | -dhve |
| 3rd | -ti | -tas | -anti | -te | -āte | -ante |
The paradigm for the tense-aspect system in Sanskrit is the three-way contrast between the "present", the "aorist" and the "perfect" architecture.[221] Vedic Sanskrit is more elaborate and had several additional tenses. For example, the Rigveda includes perfect and a marginal pluperfect. Classical Sanskrit simplifies the "present" system down to two tenses, the perfect and the imperfect, while the "aorist" stems retain the aorist tense and the "perfect" stems retain the perfect and marginal pluperfect.[221] The classical version of the language has elaborate rules for both voice and the tense-aspect system to emphasize clarity, and this is more elaborate than other Indo-European languages. The evolution of these systems can be seen from the earliest layers of the Vedic literature to the late Vedic literature.[222]
Gender, mood[edit]
Sanskrit recognizes three numbers—singular, dual, and plural.[218] The dual is a fully functioning category, used beyond naturally paired objects such as hands or eyes, extending to any collection of two. The elliptical dual is notable in the Vedic Sanskrit, according to Jamison, where a noun in the dual signals a paired opposition.[218] Illustrations include dyāvā (literally, "the two heavens" for heaven-and-earth), mātarā (literally, "the two mothers" for mother-and-father).[218] A verb may be singular, dual or plural, while the person recognized in the language are forms of "I", "you", "he/she/it", "we" and "they".[216]
There are three persons in Sanskrit: first, second and third.[214] Sanskrit uses the 3×3 grid formed by the three numbers and the three persons parameters as the paradigm and the basic building block of its verbal system.[222]
The Sanskrit language incorporates three genders: feminine, masculine and neuter.[218] All nouns have inherent gender, but with some exceptions, personal pronouns have no gender. Exceptions include demonstrative and anaphoric pronouns.[218] Derivation of a word is used to express the feminine. Two most common derivations come from feminine-forming suffixes, the -ā- (आ, Rādhā) and -ī- (ई, Rukmīnī). The masculine and neuter are much simpler, and the difference between them is primarily inflectional.[218][223] Similar affixes for the feminine are found in many Indo-European languages, states Burrow, suggesting links of the Sanskrit to its PIE heritage.[224]
Pronouns in Sanskrit include the personal pronouns of the first and second persons, unmarked for gender, and a larger number of gender-distinguishing pronouns and adjectives.[217] Examples of the former include ahám (first singular), vayám (first plural) and yūyám (second plural). The latter can be demonstrative, deictic or anaphoric.[217] Both the Vedic and Classical Sanskrit share the sá/tám pronominal stem, and this is the closest element to a third person pronoun and an article in the Sanskrit language, states Jamison.[217]
Indicative, potential and imperative are the three mood forms in Sanskrit.[216]
Prosody, meter[edit]
The Sanskrit language formally incorporates poetic metres.[225] By the late Vedic era, this developed into a field of study and it was central to the composition of the Hindu literature including the later Vedic texts. This study of Sanskrit prosody is called chandas and considered as one of the six Vedangas, or limbs of Vedic studies.[225][226]
Sanskrit prosody includes linear and non-linear systems.[227] The system started off with seven major metres, according to Annette Wilke and Oliver Moebus, called the "seven birds" or "seven mouths of Brihaspati", and each had its own rhythm, movements and aesthetics wherein a non-linear structure (aperiodicity) was mapped into a four verse polymorphic linear sequence.[228] A syllable in Sanskrit is classified as either laghu (light) or guru (heavy). This classification is based on a matra (literally, "count, measure, duration"), and typically a syllable that ends in a short vowel is a light syllable, while those that end in consonant, anusvara or visarga are heavy. The classical Sanskrit found in Hindu scriptures such as the Bhagavad Gita and many texts are so arranged that the light and heavy syllables in them follow a rhythm, though not necessarily a rhyme.[229][230][note 18]
Sanskrit metres include those based on a fixed number of syllables per verse, and those based on fixed number of morae per verse.[232] The Vedic Sanskrit employs fifteen metres, of which seven are common, and the most frequent are three (8-, 11- and 12-syllable lines).[233] The Classical Sanskrit deploys both linear and non-linear metres, many of which are based on syllables and others based on diligently crafted verses based on repeating numbers of morae (matra per foot).[233]
There is no word without meter,
nor is there any meter without words.
—Natya Shastra[234]
Meter and rhythm is an important part of the Sanskrit language. It may have played a role in helping preserve the integrity of the message and Sanskrit texts. The verse perfection in the Vedic texts such as the verse Upanishads[note 19] and post-Vedic Smriti texts are rich in prosody. This feature of the Sanskrit language led some Indologists from the 19th century onwards to identify suspected portions of texts where a line or sections are off the expected metre.[235][236][note 20]
The meter-feature of the Sanskrit language embeds another layer of communication to the listener or reader. A change in metres has been a tool of literary architecture and an embedded code to inform the reciter and audience that it marks the end of a section or chapter.[240] Each section or chapter of these texts uses identical metres, rhythmically presenting their ideas and making it easier to remember, recall and check for accuracy.[240] Authors coded a hymn's end by frequently using a verse of a metre different than that used in the hymn's body.[240] However, Hindu tradition does not use the Gayatri metre to end a hymn or composition, possibly because it has enjoyed a special level of reverence in Hinduism.[240]
Writing system[edit]

The early history of writing Sanskrit and other languages in ancient India is a problematic topic despite a century of scholarship, states Richard Salomon—an epigraphist and Indologist specializing in Sanskrit and Pali literature.[241] The earliest possible script from the Indian subcontinent is from the Indus Valley Civilization (3rd/2nd millennium BCE), but this script – if it is a script – remains undeciphered. If any scripts existed in the Vedic period, they have not survived. Scholars generally accept that Sanskrit was spoken in an oral society, and that an oral tradition preserved the extensive Vedic and Classical Sanskrit literature.[242] Other scholars such as Jack Goody state that the Vedic Sanskrit texts are not the product of an oral society, basing this view by comparing inconsistencies in the transmitted versions of literature from various oral societies such as the Greek, Serbian, and other cultures, then noting that the Vedic literature is too consistent and vast to have been composed and transmitted orally across generations, without being written down.[243][244]
Lipi is the term in Sanskrit which means "writing, letters, alphabet". It contextually refers to scripts, the art or any manner of writing or drawing.[245] The term, in the sense of a writing system, appears in some of the earliest Buddhist, Hindu, and Jaina texts. Pāṇini's Astadhyayi, composed sometime around the 5th or 4th century BCE, for example, mentions lipi in the context of a writing script and education system in his times, but he does not name the script.[245][89][246] Several early Buddhist and Jaina texts, such as the Lalitavistara Sūtra and Pannavana Sutta include lists of numerous writing scripts in ancient India.[note 21] The Buddhist texts list the sixty four lipi that the Buddha knew as a child, with the Brahmi script topping the list. "The historical value of this list is however limited by several factors", states Salomon. The list may be a later interpolation.[248][note 22] The Jain canonical texts such as the Pannavana Sutta—probably older than the Buddhist texts—list eighteen writing systems, with the Brahmi topping the list and Kharotthi (Kharoshthi) listed as fourth. The Jaina text elsewhere states that the "Brahmi is written in 18 different forms", but the details are lacking.[250] However, the reliability of these lists has been questioned and the empirical evidence of writing systems in the form of Sanskrit or Prakrit inscriptions dated prior to the 3rd century BCE has not been found. If the ancient surface for writing Sanskrit was palm leaves, tree bark and cloth—the same as those in later times, these have not survived.[251][note 23] According to Salomon, many find it difficult to explain the "evidently high level of political organization and cultural complexity" of ancient India without a writing system for Sanskrit and other languages.[251][note 24]
The oldest datable writing systems for Sanskrit are the Brāhmī script, the related Kharoṣṭhī script and the Brahmi derivatives.[254][255] The Kharosthi was used in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent and it became extinct, while the Brahmi was used in all over the subcontinent along with regional scripts such as Old Tamil.[256] Of these, the earliest records in the Sanskrit language are in Brahmi, a script that later evolved into numerous related Indic scripts for Sanskrit, along with Southeast Asian scripts (Burmese, Thai, Lao, Khmer, others) and many extinct Central Asian scripts such as those discovered along with the Kharosthi in the Tarim Basin of western China and in Uzbekistan.[257] The most extensive inscriptions that have survived into the modern era are the rock edicts and pillar inscriptions of the 3rd-century BCE Mauryan emperor Ashoka, but these are not in Sanskrit.[258][note 25]
Scripts[edit]
Over the centuries, and across countries, a number of scripts have been used to write Sanskrit.
Brahmi script[edit]

The Brahmi script for writing Sanskrit is a "modified consonant-syllabic" script. The graphic syllable is its basic unit, and this consists of a consonant with or without diacritic modifications.[260] Since the vowel is an integral part of the consonants, and given the efficiently compacted, fused consonant cluster morphology for Sanskrit words and grammar, the Brahmi and its derivative writing systems deploy ligatures, diacritics and relative positioning of the vowel to inform the reader how the vowel is related to the consonant and how it is expected to be pronounced for clarity.[255][261][note 27] This feature of Brahmi and its modern Indic script derivatives makes it difficult to classify it under the main script types used for the writing systems for most of the world's languages, namely logographic, syllabic and alphabetic.[255]
The Brahmi script evolved into "a vast number of forms and derivatives", states Richard Salomon, and in theory, Sanskrit "can be represented in virtually any of the main Brahmi-based scripts and in practice it often is".[262] Sanskrit does not have a native script. Being a phonetic language, it can be written in any precise script that efficiently maps unique human sounds to unique symbols.[clarification needed] From the ancient times, it has been written in numerous regional scripts in South and Southeast Asia. Most of these are descendants of the Brahmi script.[263] The earliest datable varnamala Brahmi alphabet system, found in later Sanskrit texts, is from the 2nd century BCE, in the form of a terracotta plaque found in Sughana, Haryana. It shows a "schoolboy's writing lessons", states Salomon.[264][265]
Nagari script[edit]
Many modern era manuscripts are written and available in the Nagari script, whose form is attestable to the 1st millennium CE.[266] The Nagari script is the ancestor of Devanagari (north India), Nandinagari (south India) and other variants. The Nāgarī script was in regular use by 7th century CE, and had fully evolved into Devanagari and Nandinagari[267] scripts by about the end of the first millennium of the common era.[268][269] The Devanagari script, states Banerji, became more popular for Sanskrit in India since about the 18th century.[270] However, Sanskrit does have special historical connection to the Nagari script as attested by the epigraphical evidence.[271]
The Nagari script has been thought as a north Indian script for Sanskrit as well as the regional languages such as Hindi, Marathi and Nepali. However, it has had a "supra-local" status as evidenced by 1st-millennium CE epigraphy and manuscripts discovered all over India and as far as Sri Lanka, Burma, Indonesia and in its parent form called the Siddhamatrka script found in manuscripts of East Asia.[272] The Sanskrit and Balinese languages Sanur inscription on Belanjong pillar of Bali (Indonesia), dated to about 914 CE, is in part in the Nagari script.[273]
The Nagari script used for Classical Sanskrit has the fullest repertoire of characters consisting of fourteen vowels and thirty three consonants. For the Vedic Sanskrit, it has two more allophonic consonantal characters (the intervocalic ळ ḷa, and ळ्ह ḷha).[272] To communicate phonetic accuracy, it also includes several modifiers such as the anusvara dot and the visarga double dot, punctuation symbols and others such as the halanta sign.[272]
Other writing systems[edit]
Other scripts such as Gujarati, Bangla, Odia and major south Indian scripts, states Salomon, "have been and often still are used in their proper territories for writing Sanskrit".[266] These and many Indian scripts look different to the untrained eye, but the differences between Indic scripts is "mostly superficial and they share the same phonetic repertoire and systemic features", states Salomon.[274] They all have essentially the same set of eleven to fourteen vowels and thirty-three consonants as established by the Sanskrit language and attestable in the Brahmi script. Further, a closer examination reveals that they all have the similar basic graphic principles, the same varnamala (literally, "garland of letters") alphabetic ordering following the same logical phonetic order, easing the work of historic skilled scribes writing or reproducing Sanskrit works across the Indian subcontinent.[275][note 28] The Sanskrit language written in some Indic scripts exaggerate angles or round shapes, but this serves only to mask the underlying similarities. Nagari script favours symmetry set with squared outlines and right angles. In contrast, Sanskrit written in the Bangla script emphasizes the acute angles while the neighbouring Odia script emphasizes rounded shapes and uses cosmetically appealing "umbrella-like curves" above the script symbols.[277]

In the south, where Dravidian languages predominate, scripts used for Sanskrit include the Kannada, Telugu, Malayalam and Grantha alphabets.
Transliteration schemes, Romanisation[edit]
Since the late 18th century, Sanskrit has been transliterated using the Latin alphabet. The system most commonly used today is the IAST (International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration), which has been the academic standard since 1888. ASCII-based transliteration schemes have also evolved because of difficulties representing Sanskrit characters in computer systems. These include Harvard-Kyoto and ITRANS, a transliteration scheme that is used widely on the Internet, especially in Usenet and in email, for considerations of speed of entry as well as rendering issues. With the wide availability of Unicode-aware web browsers, IAST has become common online. It is also possible to type using an alphanumeric keyboard and transliterate to Devanagari using software like Mac OS X's international support.
European scholars in the 19th century generally preferred Devanagari for the transcription and reproduction of whole texts and lengthy excerpts. However, references to individual words and names in texts composed in European Languages were usually represented with Roman transliteration. From the 20th century onwards, because of production costs, textual editions edited by Western scholars have mostly been in Romanised transliteration.[278]
Epigraphy[edit]
The earliest known stone inscriptions in Sanskrit are in the Brahmi script from the first century BCE.[30][note 29][note 30] These include the Ayodhyā (Uttar Pradesh) and Hāthībādā-Ghosuṇḍī (near Chittorgarh, Rajasthan) inscriptions.[30][281] Both of these, states Salomon, are "essentially standard" and "correct Sanskrit", with a few exceptions reflecting an "informal Sanskrit usage".[30] Other important Hindu inscriptions dated to the 1st century BCE, in relatively accurate classical Sanskrit and Brahmi script are the Yavanarajya inscription on a red sandstone slab and the long Naneghat inscription on the wall of a cave rest stop in the Western Ghats.[282]
Besides these few examples from the 1st century BCE, the earliest Sanskrit and hybrid dialect inscriptions are found in Mathura (Uttar Pradesh).[283] These date to the 1st and 2nd century CE, states Salomon, from the time of the Indo-Scythian Northern Satraps and the subsequent Kushan Empire.[note 31] These are also in the Brahmi script.[285] The earliest of these, states Salomon, are attributed to Ksatrapa Sodasa from the early years of 1st century CE. Of the Mathura inscriptions, the most significant is the Mora Well Inscription.[285] In a manner similar to the Hathibada inscription, the Mora well inscription is a dedicatory inscription and is linked to the cult of the Vrishni heroes: it mentions a stone shrine (temple), pratima (murti, images) and calls the five Vrishnis as bhagavatam.[285][286] There are many other Mathura Sanskrit inscriptions in Brahmi script overlapping the era of Indo-Scythian Northern Satraps and early Kushanas.[287] Other significant 1st-century inscriptions in reasonably good classical Sanskrit in the Brahmi script include the Vasu Doorjamb Inscription and the Mountain Temple inscription.[288] The early ones are related to the Brahmanical, except for the inscription from Kankali Tila which may be Jaina, but none are Buddhist.[289][290] A few of the later inscriptions from the 2nd century CE include Buddhist Sanskrit, while others are in "more or less" standard Sanskrit and related to the Brahmanical tradition.[291]
In Maharashtra and Gujarat, Brahmi script Sanskrit inscriptions from the early centuries of the common era exist at the Nasik Caves site, near the Girnar mountain of Junagadh and elsewhere such as at Kanakhera, Kanheri, and Gunda.[292] The Nasik inscription dates to the mid-1st century CE, is a fair approximation of standard Sanskrit and has hybrid features.[292] The Junagadh rock inscription of Western Satraps ruler Rudradaman I (c. 150 CE, Gujarat) is the first long poetic-style inscription in "more or less" standard Sanskrit that has survived into the modern era. It represents a turning point in the history of Sanskrit epigraphy, states Salomon.[293][note 32] Though no similar inscriptions are found for about two hundred years after the Rudradaman reign, it is important because its style is the prototype of the eulogy-style Sanskrit inscriptions found in the Gupta Empire era.[293] These inscriptions are also in the Brahmi script.[294]
The Nagarjunakonda inscriptions are the earliest known substantial South Indian Sanskrit inscriptions, probably from the late 3rd century or early 4th century CE, or both.[295] These inscriptions are related to Buddhism and the Shaivism tradition of Hinduism.[296] A few of these inscriptions from both traditions are verse-style in the classical Sanskrit language, while some such as the pillar inscription is written in prose and a hybridized Sanskrit language.[295] An earlier hybrid Sanskrit inscription found on Amaravati slab is dated to the late 2nd century, while a few later ones include Sanskrit inscriptions along with Prakrit inscriptions related to Hinduism and Buddhism.[297] After the 3rd century CE, Sanskrit inscriptions dominate and many have survived.[298] Between the 4th and 7th centuries CE, south Indian inscriptions are exclusively in the Sanskrit language.[299] In the eastern regions of the Indian subcontinent, scholars report minor Sanskrit inscriptions from the 2nd century, these being fragments and scattered. The earliest substantial true Sanskrit language inscription of Susuniya (West Bengal) is dated to the 4th century.[300] Elsewhere, such as Dehradun (Uttarakhand), inscriptions in more or less correct classical Sanskrit inscriptions are dated to the 3rd century.[300]
According to Salomon, the 4th-century reign of Samudragupta was the turning point when the classical Sanskrit language became established as the "epigraphic language par excellence" of the Indian world.[301] These Sanskrit language inscriptions are either "donative" or "panegyric" records. Generally in accurate classical Sanskrit, they deploy a wide range of regional Indic writing systems extant at the time.[302] They record the donation of a temple or stupa, images, land, monasteries, pilgrim's travel record, public infrastructure such as water reservoir and irrigation measures to prevent famine. Others praise the king or the donor in lofty poetic terms.[303] The Sanskrit language of these inscriptions is written on stone, various metals, terracotta, wood, crystal, ivory, shell and cloth.[304][note 33]
The evidence of the use of the Sanskrit language in Indic writing systems appears in southeast Asia in the first half of the 1st millennium CE.[307] A few of these in Vietnam are bilingual where both the Sanskrit and the local language is written in the Indian alphabet. Early Sanskrit language inscriptions in Indic writing systems are dated to the 4th century in Malaysia, 5th to 6th centuries in Thailand near Si Thep and the Sak River, early 5th century in Kutai (east Borneo) and mid-5th century in west Java (Indonesia).[307] Both major writing systems for Sanskrit, the North Indian and South Indian scripts, have been discovered in southeast Asia, but the Southern variety with its rounded shapes are far more common.[308] The Indic scripts, particularly the Pallava script prototype,[309] spread and ultimately evolved into Mon-Burmese, Khmer, Thai, Laos, Sumatran, Celebes, Javanese and Balinese scripts.[310][311] From about the 5th century, Sanskrit inscriptions become common in many parts of South Asia and Southeast Asia, with significant discoveries in Nepal, Vietnam and Cambodia.[301]
Texts[edit]
Sanskrit has been written in various scripts on a variety of media such as palm leaves, cloth, paper, rock and metal sheets, from ancient times.[312]
| Tradition | Sanskrit texts, genre or collection | Example | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hinduism | Scriptures | Vedas, Upanishads, Agamas, Bhagavad Gita | [313][314] |
| Language, Grammar | Ashtadhyayi | [315][316] | |
| Law | Dharmasutras, Dharmasastras | [317] | |
| State craft, politics | Arthasastra | [318] | |
| Timekeeping and Mathematics | Kalpa, Jyotisha, Ganitasastra | [319][320] | |
| Life sciences, health | Ayurveda, Sushruta samhita, Caraka samhita | [321][322] | |
| Sex, emotions | Kamasastra | [323] | |
| Epics | Ramayana, Mahabharata, Raghuvamsa | [324][325] | |
| Gnomic and didactic literature | Subhashitas | [326] | |
| Drama, dance and performance arts | Natyasastra | [327][328][329] | |
| Music | Sangitasastra | [330][331] | |
| Poetics | Kavyasastra | [332] | |
| Mythology | Puranas | [333] | |
| Mystical speculations, Philosophy | Darsana, Samkhya, Yoga (philosophy), Nyaya, Vaisheshika, Mimamsa, Vedanta, Vaishnavism, Shaivism, Shaktism, Smarta Tradition and others | [334] | |
| Krishi (Agriculture and food) | Krsisastra | [335] | |
| Vastu, Shilpa (Design, Architecture) | Shilpasastra | [336][337] | |
| Temples, Sculpture | Brihatsamhita | [338] | |
| Samskara (rites-of-passage) | Grhyasutras | [339] | |
| Buddhism | Scripture, Monastic law | Tripitaka,[note 34] Mahayana Buddhist texts, others | [340][341][342] |
| Jainism | Theology, philosophy | Tattvartha Sutra, Mahapurana and others | [343][344] |
Influence on other languages[edit]
For nearly 2,000 years, Sanskrit was the language of a cultural order that exerted influence across South Asia, Inner Asia, Southeast Asia, and to a certain extent East Asia.[148] A significant form of post-Vedic Sanskrit is found in the Sanskrit of Indian epic poetry—the Ramayana and Mahabharata. The deviations from Pāṇini in the epics are generally considered to be on account of interference from Prakrits, or innovations, and not because they are pre-Paninian.[345] Traditional Sanskrit scholars call such deviations ārṣa (आर्ष), meaning 'of the ṛṣis', the traditional title for the ancient authors. In some contexts, there are also more "prakritisms" (borrowings from common speech) than in Classical Sanskrit proper. Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit is a literary language heavily influenced by the Middle Indo-Aryan languages, based on early Buddhist Prakrit texts which subsequently assimilated to the Classical Sanskrit standard in varying degrees.[346]
Indic languages[edit]
Sanskrit has greatly influenced the languages of India that grew from its vocabulary and grammatical base; for instance, Hindi is a "Sanskritised register" of Hindustani. All modern Indo-Aryan languages, as well as Munda and Dravidian languages have borrowed many words either directly from Sanskrit (tatsama words), or indirectly via middle Indo-Aryan languages (tadbhava words). Words originating in Sanskrit are estimated at roughly fifty percent of the vocabulary of modern Indo-Aryan languages, as well as the literary forms of Malayalam and Kannada.[347] Literary texts in Telugu are lexically Sanskrit or Sanskritised to an enormous extent, perhaps seventy percent or more.[348] Marathi is another prominent language in Western India, that derives most of its words and Marathi grammar from Sanskrit.[349] Sanskrit words are often preferred in the literary texts in Marathi over corresponding colloquial Marathi word.[350]
Interaction with other languages[edit]
Buddhist Sanskrit has had a considerable influence on East Asian languages such as Chinese, state William Wang and Chaofen Sun.[351] Many words have been adopted from Sanskrit into the Chinese, both in its historic religious discourse and everyday use.[351][note 35] This process likely started about 200 CE and continued through about 1400 CE, with the efforts of monks such as Yuezhi, Anxi, Kangju, Tianzhu, Yan Fodiao, Faxian, Xuanzang and Yijing.[351] Further, as the Chinese language and culture influenced the rest of East Asia, the ideas in Sanskrit texts and some of its linguistic elements migrated further.[352][353]
Sanskrit has also influenced Sino-Tibetan languages, mostly through translations of Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit. Many terms were transliterated directly and added to the Chinese vocabulary. Chinese words like 剎那 chànà (Devanagari: क्षण kṣaṇa 'instantaneous period') were borrowed from Sanskrit. Many Sanskrit texts survive only in Tibetan collections of commentaries to the Buddhist teachings, the Tengyur.[354]
Sanskrit was a language for religious purposes and for the political elite in parts of medieval era Southeast Asia, Central Asia and East Asia.[139] In Southeast Asia, languages such as Thai and Lao contain many loanwords from Sanskrit, as does Khmer. Many Sanskrit loanwords are also found in Austronesian languages, such as Javanese, particularly the older form in which nearly half the vocabulary is borrowed.[355] Other Austronesian languages, such as traditional Malay and modern Indonesian, also derive much of their vocabulary from Sanskrit. Similarly, Philippine languages such as Tagalog have some Sanskrit loanwords, although more are derived from Spanish. A Sanskrit loanword encountered in many Southeast Asian languages is the word bhāṣā, or spoken language, which is used to refer to the names of many languages.[356] English also has words of Sanskrit origin.
Sanskrit has also influenced the religious register of Japanese mostly through transliterations. These were borrowed from Chinese transliterations.[357] In particular, the Shingon (lit. "True Words") sect of esoteric Buddhism has been relying on Sanskrit and original Sanskrit mantras and writings, as a means of realizing Buddhahood.[358]
Modern era[edit]
Liturgy, ceremonies and meditation[edit]
Sanskrit is the sacred language of various Hindu, Buddhist, and Jain traditions. It is used during worship in Hindu temples. In Newar Buddhism, it is used in all monasteries, while Mahayana and Tibetan Buddhist religious texts and sutras are in Sanskrit as well as vernacular languages. Some of the revered texts of Jainism including the Tattvartha sutra, Ratnakaranda śrāvakācāra, the Bhaktamara Stotra and the Agamas are in Sanskrit. Further, states Paul Dundas, Sanskrit mantras and Sanskrit as a ritual language was commonplace among Jains throughout their medieval history.[359]
Many Hindu rituals and rites-of-passage such as the "giving away the bride" and mutual vows at weddings, a baby's naming or first solid food ceremony and the goodbye during a cremation invoke and chant Sanskrit hymns.[360] Major festivals such as the Durga Puja ritually recite entire Sanskrit texts such as the Devi Mahatmya every year particularly amongst the numerous communities of eastern India.[361][362] In the south, Sanskrit texts are recited at many major Hindu temples such as the Meenakshi Temple.[363] According to Richard H. Davis, a scholar of Religion and South Asian studies, the breadth and variety of oral recitations of the Sanskrit text Bhagavad Gita is remarkable. In India and beyond, its recitations include "simple private household readings, to family and neighborhood recitation sessions, to holy men reciting in temples or at pilgrimage places for passersby, to public Gita discourses held almost nightly at halls and auditoriums in every Indian city".[364]
Literature and arts[edit]
More than 3,000 Sanskrit works have been composed since India's independence in 1947.[365] Much of this work has been judged of high quality, in comparison to both classical Sanskrit literature and modern literature in other Indian languages.[366][367]
The Sahitya Akademi has given an award for the best creative work in Sanskrit every year since 1967. In 2009, Satya Vrat Shastri became the first Sanskrit author to win the Jnanpith Award, India's highest literary award.[368]
Sanskrit is used extensively in the Carnatic and Hindustani branches of classical music. Kirtanas, bhajans, stotras, and shlokas of Sanskrit are popular throughout India. The samaveda uses musical notations in several of its recessions.[369]
In Mainland China, musicians such as Sa Dingding have written pop songs in Sanskrit.[370]
Numerous loan Sanskrit words are found in other major Asian languages. For example, Filipino,[371] Cebuano,[372] Lao, Khmer[373] Thai and its alphabets, Malay, Indonesian (old Javanese-English dictionary by P.J. Zoetmulder contains over 25,500 entries), and even in English.
Over 90 weeklies, fortnightlies and quarterlies are published in Sanskrit. Sudharma, a daily newspaper in Sanskrit, has been published out of Mysore, India, since 1970, while Sanskrit Vartman Patram and Vishwasya Vrittantam started in Gujarat during the last five years.[374] Since 1974, there has been a short daily news broadcast on state-run All India Radio.[374] These broadcasts are also made available on the internet on AIR's website.[375][376] Sanskrit news is broadcast on TV and on the internet through the DD National channel at 6:55 AM IST.[377]
Schools and contemporary status[edit]

Sanskrit is one the 22 languages of the Eighth Schedule to the Constitution of India.[253] Sanskrit is a studied school subject in contemporary India, but scarce as a first language. In the 2001 Census of India, 14,135 Indians reported Sanskrit to be their first language.[378] In the 2011 census, 24,821 people out of about 1.21 billion reported Sanskrit to be their first language.[379][note 36][note 37] According to the 2011 national census of Nepal, 1,669 people use Sanskrit as their first language.[3]
The Central Board of Secondary Education of India (CBSE), along with several other state education boards, has made Sanskrit an alternative option to the state's own official language as a second or third language choice in the schools it governs. In such schools, learning Sanskrit is an option for grades 5 to 8 (Classes V to VIII). This is true of most schools affiliated with the Indian Certificate of Secondary Education (ICSE) board, especially in states where the official language is Hindi. Sanskrit is also taught in traditional gurukulas throughout India.[384]
A number of colleges and universities in India have dedicated departments for Sanskrit studies.
In the West[edit]
St James Junior School in London, England, offers Sanskrit as part of the curriculum.[385] In the United States, since September 2009, high school students have been able to receive credits as Independent Study or toward Foreign Language requirements by studying Sanskrit, as part of the "SAFL: Samskritam as a Foreign Language" program coordinated by Samskrita Bharati.[386] In Australia, the Sydney private boys' high school Sydney Grammar School offers Sanskrit from years 7 through to 12, including for the Higher School Certificate.[387] Other schools included the Ficino School in Auckland, New Zealand; St James Preparatory Schools in Cape Town, Durban and Johannesburg, South Africa; John Colet School, Sydney, Australia; Erasmus School, Melbourne, Australia.[388][389][390]
European studies and discourse[edit]
European scholarship in Sanskrit, begun by Heinrich Roth (1620–1668) and Johann Ernst Hanxleden (1681–1731), is considered responsible for the discovery of an Indo-European language family by Sir William Jones (1746–1794). This research played an important role in the development of Western philology, or historical linguistics.[391]
The 18th- and 19th-century speculations about the possible links of Sanskrit to ancient Egyptian language were later proven to be wrong, but it fed an orientalist discourse both in the form Indophobia and Indophilia, states Trautmann.[392] Sanskrit writings, when first discovered, were imagined by Indophiles to potentially be "repositories of the primitive experiences and religion of the human race, and as such confirmatory of the truth of Christian scripture", as well as a key to "universal ethnological narrative".[393] The Indophobes imagined the opposite, making the counterclaim that there is little of any value in Sanskrit, portraying it as "a language fabricated by artful [Brahmin] priests", with little original thought, possibly copied from the Greeks who came with Alexander or perhaps the Persians.[394]
Scholars such as William Jones and his colleagues felt the need for systematic studies of Sanskrit language and literature. This launched the Asiatic Society, an idea that was soon transplanted to Europe starting with the efforts of Henry Thomas Colebrooke in Britain, then Alexander Hamilton who helped expand its studies to Paris and thereafter his student Friedrich Schlegel who introduced Sanskrit to the universities of Germany. Schlegel nurtured his own students into influential European Sanskrit scholars, particularly through Franz Bopp and Friedrich Max Muller. As these scholars translated the Sanskrit manuscripts, the enthusiasm for Sanskrit grew rapidly among European scholars, states Trautmann, and chairs for Sanskrit "were established in the universities of nearly every German statelet" creating a competition for Sanskrit experts.[395]
Symbolic usage[edit]
In India, Indonesia, Nepal, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, and Southeast Asia, Sanskrit phrases are widely used as mottoes for various national, educational and social organisations:
- India: Satyameva Jayate (सत्यमेव जयते) meaning: Truth alone triumphs.[396]
- Nepal: Janani Janmabhūmischa Swargādapi Garīyasī meaning: Mother and motherland are superior to heaven.[citation needed]
- Indonesia: In Indonesia, Sanskrit are usually widely used as terms and mottoes of the armed forces and other national organizations (See: Indonesian Armed Forces mottoes). Rastra Sewakottama (राष्ट्र सेवकोत्तम; People's Main Servants) is the official motto of the Indonesian National Police, Tri Dharma Eka Karma (त्रिधर्म एक कर्म) is the official motto of the Indonesian Military, Kartika Eka Paksi (कार्तिक एक पक्षी; Unmatchable Bird with Noble Goals) is the official motto of the Indonesian Army,[397] Adhitakarya Mahatvavirya Nagarabhakti (अधीतकार्य महत्ववीर्य नगरभक्ति; "Hard-working Knights Serving Bravery as Nations Hero") is the official motto of the Indonesian Military Academy,[398] Upakriya Labdha Prayojana Balottama (उपक्रिया लब्ध प्रयोजन बालोत्तम; "Purpose of The Unit is to Give The Best Service to The Nation by Finding The Perfect Soldier") is the official motto of the Army Psychological Corps, Karmanye Vadikaraste Mafalesu Kadatjana (कर्मण्येवाधिकारस्ते मा फलेषु कदाचन; "Working Without Counting The Profit and Loss") is the official motto of the Air-Force Special Forces (Paskhas),[399] Jalesu Bhumyamca Jayamahe (जलेषु भूम्यम्च जयमहे; on The Sea and Land We Are Glorious") is the official motto of the Indonesian Marine Corps,[400] and there are more units and organizations in Indonesia either Armed Forces or civil which use the Sanskrit language respectively as their mottoes and other purposes.
- Many of India's and Nepal's scientific and administrative terms use Sanskrit. The Indian guided missile program that was commenced in 1983 by the Defence Research and Development Organisation has named the five missiles (ballistic and others) that it developed Prithvi, Agni, Akash, Nag and the Trishul missile system. India's first modern fighter aircraft is named HAL Tejas.[citation needed]
In popular culture[edit]
Satyagraha, an opera by Philip Glass, uses texts from the Bhagavad Gita, sung in Sanskrit.[401][402] The closing credits of The Matrix Revolutions has a prayer from the Brihadaranyaka Upanishad. The song "Cyber-raga" from Madonna's album Music includes Sanskrit chants,[403] and Shanti/Ashtangi from her 1998 album Ray of Light, which won a Grammy, is the ashtanga vinyasa yoga chant.[404] The lyrics include the mantra Om shanti.[405] Composer John Williams featured choirs singing in Sanskrit for Indiana Jones and the Temple of Doom and in Star Wars: Episode I – The Phantom Menace.[406][407][better source needed] The theme song of Battlestar Galactica 2004 is the Gayatri Mantra, taken from the Rigveda.[408] The lyrics of "The Child In Us" by Enigma also contains Sanskrit verses.[409][better source needed]
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ The Old Hittite language and Mycenaean Greek, along with the Sanskrit language, are the oldest documented IE languages; of these, Old Hittite is dated to be the oldest.[20][21]
- ^ The oldest documented South Asian language is not Sanskrit, however. It is the language evidenced by the undeciphered Harappan script from the 3rd millennium BCE.[20]
- ^ More numerous inscribed Sanskrit records in Brahmi have been found near Mathura and elsewhere, but these are from the 1st century CE onwards.[31] Indian texts in Sanskrit were already in China by 402 CE, carried by the influential Buddhist pilgrim Faxian, who translated them into Chinese by 418 CE.[32][33]
- ^ Mallory and Adams illustrate the resemblance with the following words:
English Latin Greek Sanskrit
mother māter mētēr mātár-
father pater pater pitár-
brother frāter phreter bhrātar-
sister soror eor svásar-
son fīlius huius sūnú-
daughter fīlia thugátēr duhitár-
cow bōs bous gáu-
house domus do dām-
– James Mallory and Douglas Adams,The Oxford Introduction to Proto-Indo-European and the Proto-Indo-European World[55] - ^ The Mitanni treaty is generally dated to the 16th century BCE, but this date and its significance remains much debated.[69]
- ^ An example of the shared phrasal equations is the dyaus pita in Vedic Sanskrit, which means "father Heaven". The Mycenaean Greek equivalent is Zeus Pater, which evolved to Jupiter in Latin. Equivalent "paternal Heaven" phrasal equation is found in many Indo-European languages.[74]
- ^ Pāṇini's use of the term lipi has been a source of scholarly disagreements. Harry Falk in his 1993 overview states that ancient Indians neither knew nor used writing script, and Pāṇini's mention is likely a reference to Semitic and Greek scripts.[91] In his 1995 review, Salomon questions Falk's arguments and writes it is "speculative at best and hardly constitutes firm grounds for a late date for Kharoṣṭhī. The stronger argument for this position is that we have no specimen of the script before the time of Ashoka, nor any direct evidence of intermediate stages in its development; but of course this does not mean that such earlier forms did not exist, only that, if they did exist, they have not survived, presumably because they were not employed for monumental purposes before Ashoka".[92] According to Hartmut Scharfe, Lipi of Pāṇini may be borrowed from the Old Persian Dipi, in turn derived from Sumerian Dup. Scharfe adds that the best evidence, at the time of his review, is that no script was used in India, aside from the Northwest Indian subcontinent, before around 300 BCE because Indian tradition "at every occasion stresses the orality of the cultural and literary heritage."[93] Kenneth Norman states writing scripts in ancient India evolved over the long period of time like other cultures, that it is unlikely that ancient Indians developed a single complete writing system at one and the same time in the Maurya era. It is even less likely, states Norman, that a writing script was invented during Ashoka's rule, starting from nothing, for the specific purpose of writing his inscriptions and then it was understood all over South Asia where the Ashoka pillars are found.[94] Jack Goody states that ancient India likely had a "very old culture of writing" along with its oral tradition of composing and transmitting knowledge, because the Vedic literature is too vast, consistent and complex to have been entirely created, memorized, accurately preserved and spread without a written system.[95] Falk disagrees with Goody, and suggests that it is a Western presumption and inability to imagine that remarkably early scientific achievements such as Pāṇini's grammar (5th to 4th century BCE), and the creation, preservation and wide distribution of the large corpus of the Brahmanic Vedic literature and the Buddhist canonical literature, without any writing scripts. Johannes Bronkhorst disagrees with Falk, and states, "Falk goes too far. It is fair to expect that we believe that Vedic memorisation—though without parallel in any other human society—has been able to preserve very long texts for many centuries without losing a syllable. [...] However, the oral composition of a work as complex as Pāṇini's grammar is not only without parallel in other human cultures, it is without parallel in India itself. [...] It just will not do to state that our difficulty in conceiving any such thing is our problem".[96]
- ^ Scholars have variously dated the Ramayana from about 750 BCE to 300 CE, the wide range depending on whether the estimate is for the earliest version or for the versions that have survived into the modern era. According to Sanskrit epics scholar John Brockington, the earliest layer of the Ramayana epic was composed about the 5th to the 4th centuries BCE. Other recent scholarly estimates are around the 4th century BCE, give or take a century.[105]
- ^ Pali is also an extinct language.[111]
- ^ The Indian Mission for Manuscripts initiative has already counted over 5 million manuscripts. The thirty million estimate is of David Pingree, a manuscriptologist and historian. – Peter M. Scharf[120]
- ^ A celebrated work on the philosophy of language is the Vakyapadiya by the 5th-century Hindu scholar Bhartrhari.[123][126][127]
- ^ The oldest surviving Sanskrit inscription in the Kathmandu valley is dated to 464 CE.[178]
- ^ Sanskrit is written in many scripts. Sounds in grey are not phonemic.
- ^ Sanskrit is written in many scripts. Sounds in grey are not phonemic.
- ^ The "root + affix" is called the "stem".[216]
- ^ Other equivalents: bharāmi (I carry), bharati (he carries), bharāmas (we carry).[55] Similar morphology is found in some other Indo-European languages; for example, in the Gothic language, baira (I carry), bairis (you carry), bairiþ (he carries).
- ^ Ruppel gives the following endings for the "present indicative active" in the Sanskrit language: 1st dual: -vaḥ, 1st plural: -maḥ, 2nd dual: -thaḥ, 2nd plural: -tha and so on.[100]
- ^ The Sanskrit in the Indian epics such as the Mahabharata and the Ramayana are all in meter, and the structure of the metrics has attracted scholarly studies since the 19th century.[231]
- ^ Kena, Katha, Isha, Shvetashvatara and Mundaka Upanishads are examples of verse-style ancient Upanishads.
- ^ Sudden or significant changes in metre, wherein the metre of succeeding sections return to earlier sections, suggest a corruption of the message, interpolations and insertion of text into a Sanskrit manuscript. It may also reflect that the text is a compilation of works of different authors and time periods.[237][238][239]
- ^ The Buddhist text Lalitavistara Sūtra describes the young Siddhartha—the future Buddha—to have mastered philology and scripts at a school from Brahmin Lipikara and Deva Vidyasinha.[247]
- ^ A version of this list of sixty-four ancient Indian scripts is found in the Chinese translation of an Indian Buddhist text, and this translation has been dated to 308 CE.[249]
- ^ The Greek Nearchos who visited ancient India with the army of Alexander the Great in the 4th century BCE, mentions that Indians wrote on cloth, but Nearchos could have confused Aramaic writers with the Indians.[252]
- ^ Salomon writes, in The World's Writing Systems edited by Peter Daniels, that "many scholars feel that the origins of these scripts must have gone back further than this [mid-3rd century BCE Ashoka inscriptions], but there is no conclusive proof".[253]
- ^ Minor inscriptions discovered in the 20th century may be older, but their dating is uncertain.[258]
- ^ Salomon states that the inscription has a few scribal errors, but is essentially standard Sanskrit.[30]
- ^ Salomon illustrates this for the consonant ka which is written as "
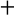 " in the Brahmi script and "क" in the Devanagari script, the vowel is marked together with the consonant before as in "कि", after "का", above "के" or below "कृ".[255]
" in the Brahmi script and "क" in the Devanagari script, the vowel is marked together with the consonant before as in "कि", after "का", above "के" or below "कृ".[255] - ^ Salomon states that these shared graphic principles that combine syllabic and alphabetic writing are distinctive for Indic scripts when contrasted with other major world languages. The only known similarity is found in the Ethiopic scripts, but Ethiopic system lacks clusters and the Indic set of full vowels signs.[276]
- ^ Some scholars date these to the 2nd century BCE.[279][280]
- ^ Prakrit inscriptions of ancient India, such as those of Ashoka, are older. Louis Renou called it "the great linguistical paradox of India" that the Sanskrit inscriptions appear later than Prakrit inscriptions, although Prakrit is considered as a descendant of the Sanskrit language.[30]
- ^ According to Salomon, towards the end of pre-Christian era, "a smattering" of standard or nearly standard Sanskrit inscriptions came into vogue, and "we may assume that these are isolated survivals of what must have been then an increasingly common practice". He adds, that the Scythian rulers of northern and western India while not the originators, were promoters of the use of Sanskrit language for inscriptions, and "their motivation in promoting Sanskrit was presumably a desire to establish themselves as legitimate Indian or at least Indianized rulers and to curry the favor of the educated Brahmanical elite".[284]
- ^ The Rudradaman inscription is "not pure classical Sanskrit", but with few epic-vernacular Sanskrit exceptions, it approaches high classical Sanskrit.[293]
- ^ The use of the Sanskrit language in epigraphy gradually dropped after the arrival and the consolidation of Islamic Delhi Sultanate rule in the late 12th century, but it remained in active epigraphical use in the south and central regions of India. By about the 14th century, with the Islamic armies conquering more of the Indian subcontinent, the use of Sanskrit language for inscriptions became rarer and it was replaced with Persian, Arabic, Dravidian and North-Indo-Aryan languages, states Salomon.[305] The Sanskrit language, particularly in bilingual formet, re-emerged in the epigraphy of Hindu kingdoms such as the Vijayanagara, Yadavas, Hoysalas, Pandyas and others that re-established themselves.[306] Some Muslim rulers such as Adil Shah also issued Sanskrit language inscriptions recording the donation of a mosque.[306]
- ^ Most Tripitaka historic texts in the Pali language, but Sanskrit Tripitaka texts have been discovered.[340]
- ^ Examples of phonetically imported Sanskrit words in Chinese include samgha (Chinese: seng), bhiksuni (ni), kasaya (jiasha), namo or namas (namo), and nirvana (niepan). The list of phonetically transcribed and semantically translated words from Sanskrit into Chinese is substantial, states Xiangdong Shi.[351]
- ^ India is linguistically diverse. Its 2001 census report listed 122 languages and their use, while the raw data returned 1,635 "rationalized mother languages" and 1,937 unclassified 'other' mother tongues.[188]
- ^ Indian newspapers have published reports about several villages, where many are learning Sanskrit and attempting to use it to some extent in everyday communication:
References[edit]
- ^ Uta Reinöhl (2016). Grammaticalization and the Rise of Configurationality in Indo-Aryan. Oxford University Press. pp. xiv, 1–16. ISBN 978-0-19-873666-0.
- ^ "Latest census figure reveals increase in Sanskrit speakers in India". 15 July 2018.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b National Population and Housing Census 2011 (PDF) (Report). 1. Kathmandu: Central Bureau of Statistics, Government of Nepal. November 2012. Archived from the original (PDF) on 28 December 2013.
- ^ Government of India, Ministry of Home Affairs. "C-17 POPULATION BY BILINGUALISM AND TRILINGUALISM".
- ^ "http://aboutworldlanguages.com/sanskrit"
- ^ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds. (2017). "Sanskrit". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History.
- ^ "dictionary.com – Sanskrit". Retrieved 11 June 2019.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e George Cardona (2012). Sanskrit Language. Encyclopaedia Britannica.
- ^ Tim Murray 2007, pp. v–vi, 1–18, 31–32, 115–116.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Harold G. Coward 1990, pp. 3–12, 36–47, 111–112, Note: Sanskrit was both a literary and spoken language in ancient India..
- ^ Damien Keown & Charles S. Prebish 2013, p. 15, Quote: "Sanskrit served as the lingua franca of ancient India, just as Latin did in medieval Europe".
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e Deshpande 2011, pp. 218–220.
- ^ A. M. Ruppel 2017, pp. 1–2, 102–104.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Ramesh Chandra Majumdar 1974, pp. 1–4.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Charles Orzech; Henrik Sørensen; Richard Payne (2011). Esoteric Buddhism and the Tantras in East Asia. BRILL Academic. pp. 985–996. ISBN 978-90-04-18491-6.; Upendra Thakur (1992). India and Japan, a Study in Interaction During 5th Cent.-14th Cent. A.D. Abhinav Publications. pp. 53–61. ISBN 978-81-7017-289-5.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Banerji 1989, pp. 595–596.
- ^ Michael C. Howard 2012, p. 21, Quote: "Sanskrit was another important lingua franca in the ancient world that was widely used in South Asia and in the context of Hindu and Buddhist religions in neighboring areas as well. [...] The spread of South Asian cultural influence to Southeast Asia, meant that Sanskrit was also used in these areas, especially in a religious context and political elites.".
- ^ Sheldon Pollock 2009, p. 14, Quote: once Sanskrit emerged from the sacerdotal environment ... it became the sole medium by which ruling elites expressed their power ... Sanskrit probably never functioned as an everyday medium of communication anywhere in the cosmopolis—not in South Asia itself, let alone Southeast Asia ... The work Sanskrit did do ... was directed above all toward articulating a form of ... politics ... as celebration of aesthetic power.".
- ^ Philipp Strazny 2013, p. 500.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Roger D. Woodard (2008). The Ancient Languages of Asia and the Americas. Cambridge University Press. pp. 1–2. ISBN 978-0-521-68494-1., Quote: "The earliest form of this 'oldest' language, Sanskrit, is the one found in the ancient Brahmanic text called the Rigveda, composed c. 1500 BC. The date makes Sanskrit one of the three earliest of the well-documented languages of the Indo-European family – the other two being Old Hittite and Myceanaean Greek – and, in keeping with its early appearance, Sanskrit has been a cornerstone in the reconstruction of the parent language of the Indo-European family – Proto-Indo-European."
- ^ Arne Hult (1991). On the Development of the Present Active Participle in Bulgarian. Institutum Slavicum Universitatis Gothoburgensis. p. 26. ISBN 978-91-86094-11-9.
- ^ Benware 1974, pp. 25–27.
- ^ Thomas Burrow 2001, pp. v & ch. 1.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Alfred C. Woolner (1986). Introduction to Prakrit. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 3–4. ISBN 978-81-208-0189-9., Quote:"If in 'Sanskrit' we include the Vedic language and all dialects of the Old Indian period, then it is true to say that all the Prakrits are derived from Sanskrit. If on the other hand 'Sanskrit' is used more strictly of the Panini-Patanjali language or 'Classical Sanskrit,' then it is untrue to say that any Prakrit is derived from Sanskrit, except that Sauraseni, the Midland Prakrit, is derived from the Old Indian dialect of the Madhyadesa on which Classical Sanskrit was mainly based."
- ^ 위로 점프: a b William Bright (2014). American Indian Linguistics and Literature. Walter De Gruyter. pp. 16–17. ISBN 978-3-11-086311-6.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Cynthia Groff (2017). The Ecology of Language in Multilingual India: Voices of Women and Educators in the Himalayan Foothills. Palgrave Macmillan UK. pp. 183–185. ISBN 978-1-137-51961-0.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Iswari P. Pandey (2015). South Asian in the Mid-South: Migrations of Literacies. University of Pittsburgh Press. pp. 85–86. ISBN 978-0-8229-8102-2.
- ^ Staal 1986.
- ^ Filliozat 2004, pp. 360–375.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e f g h Salomon 1998, pp. 86–87.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 87–89.
- ^ Henri Arvon. Faxian: Chinese Buddhist Monk. Encyclopaedia Britannica.
- ^ Robert E. Buswell Jr.; Donald S. Lopez Jr. (2013). The Princeton Dictionary of Buddhism. Princeton University Press. p. 504. ISBN 978-1-4008-4805-8.
- ^ Reinhold Grünendahl (2001). South Indian Scripts in Sanskrit Manuscripts and Prints: Grantha Tamil, Malayalam, Telugu, Kannada, Nandinagari. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. xiii–xxii. ISBN 978-3-447-04504-9.
- ^ Dhanesh Jain; George Cardona (2007). The Indo-Aryan Languages. Routledge. pp. 51–52. ISBN 978-1-135-79711-9.
- ^ Pārameśvaratantra (MS Add.1049.1) with images Archived 2016-03-08 at the Wayback Machine, Puṣkarapārameśvaratantra, University of Cambridge (2015), Quote: one of the oldest known dated Sanskrit manuscripts from South Asia, this specimen transmits a substantial portion of the Pārameśvaratantra, a scripture of the Śaiva Siddhānta, one of the Tantric theological schools that taught the worship of Śiva as "Supreme Lord" (the literal meaning of Parameśvara). [...] According to the colophon, it was copied in the year 252, which some scholars judge to be of the era established by the Nepalese king Aṃśuvarman (also known as Mānadeva), therefore corresponding to 828 CE." – a Palm Leaf manuscript at the Cambridge University Library in Late Gupta in black ink, MS Add.1049.1
- ^ Angus Stevenson & Maurice Waite 2011, p. 1275
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Shlomo Biderman 2008, p. 90.
- ^ Will Durant 1963, p. 406.
- ^ Sir Monier Monier-Williams (2005). A Sanskrit-English Dictionary: Etymologically and Philologically Arranged with Special Reference to Cognate Indo-European Languages. Motilal Banarsidass. p. 1120. ISBN 978-81-208-3105-6.
- ^ Louis Renou & Jagbans Kishore Balbir 2004, pp. 1-2.
- ^ Annette Wilke; Oliver Moebus (2011). Sound and Communication: An Aesthetic Cultural History of Sanskrit Hinduism. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 62–66 with footnotes. ISBN 978-3-11-024003-0.
- ^ Guy L. Beck 2006, pp. 117–123.
- ^ Southworth, Franklin (2004), Linguistic Archaeology of South Asia, Routledge, p. 45, ISBN 978-1-134-31777-6
- ^ Jared Klein; Brian Joseph; Matthias Fritz (2017). Handbook of Comparative and Historical Indo-European Linguistics: An International Handbook. Walter De Gruyter. pp. 318–320. ISBN 978-3-11-026128-8.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Brigitte L. M. Bauer (2017). Nominal Apposition in Indo-European: Its Forms and Functions, and its Evolution in Latin-Romance. De Gruyter. pp. 90–92, for detailed comparison of the languages, see pages 90–126. ISBN 978-3-11-046175-6.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Anna Giacalone Ramat; Paolo Ramat (2015). The Indo-European Languages. Routledge. pp. 26–31. ISBN 978-1-134-92187-4.
- ^ "Ancient Tablet Found: Oldest Readable Writing in Europe". 1 April 2011.
- ^ Jenny Rose (18 August 2011). Zoroastrianism: A Guide for the Perplexed. Bloomsbury Publishing. pp. 75–76. ISBN 978-1-4411-2236-0.
- ^ Ahmad Hasan Dani; Vadim Mikhaĭlovich Masson (1999). History of Civilizations of Central Asia. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 357–358. ISBN 978-81-208-1407-3.
- ^ Colin P. Masica 1993, p. 34.
- ^ Levin, Saul. Semitic and Indo-European, Volume 2. John Benjamins Publishing Company. p. 431.
- ^ Edwin Francis Bryant; Laurie L. Patton. The Indo-Aryan Controversy: Evidence and Inference in Indian History. Psychology Press. p. 208.
- ^ R.H. Robins (2014). General Linguistics. Routledge. pp. 346–347. ISBN 978-1-317-88763-8.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b J. P. Mallory & D. Q. Adams 2006, p. 6.
- ^ Thomas Burrow 2001, p. 6.
- ^ Colin P. Masica 1993, p. 36-38.
- ^ Thomas Burrow 2001, pp. 30–32.
- ^ Thomas Burrow 2001, pp. 30–34.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Michael Meier-Brügger (2003). Indo-European Linguistics. Walter de Gruyter. p. 20. ISBN 978-3-11-017433-5.
- ^ MacDonell 2004.
- ^ A. Berriedale Keith (1993). A history of Sanskrit literature. Motilal Banarsidass. p. 4. ISBN 978-81-208-1100-3.
- ^ Barbara A. Holdrege 2012, pp. 229–230.
- ^ Bryant 2001, pp. 66–67.
- ^ Louis Renou & Jagbans Kishore Balbir 2004, pp. 5–6.
- ^ Witzel, M (1997). Inside the texts, beyond the texts: New approaches to the study of the Vedas (PDF). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. p. 9. Retrieved 17 July 2018.
- ^ Witzel, M (1997). Inside the texts, beyond the texts: New approaches to the study of the Vedas (PDF). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. pp. 16–17. Retrieved 17 July 2018.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Signe Cohen (2017). The Upanisads: A Complete Guide. Taylor & Francis. pp. 11–17. ISBN 978-1-317-63696-0.
- ^ Edwin Bryant (2001). The Quest for the Origins of Vedic Culture: The Indo-Aryan Migration Debate. Oxford University Press. p. 249. ISBN 978-0-19-803151-2.
- ^ Andrew Robinson (2014). India: A Short History. Thames & Hudson. pp. 56–57. ISBN 978-0-500-77195-2.
- ^ Roger D. Woodard (2008). The Ancient Languages of Asia and the Americas. Cambridge University Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-0-521-68494-1.
- ^ John Jeffrey Lowe (2015). Participles in Rigvedic Sanskrit: The Syntax and Semantics of Adjectival Verb Forms. Oxford University Press. pp. 2–3. ISBN 978-0-19-870136-1.
- ^ Stephanie W. Jamison & Joel P. Brereton 2014, pp. 10–11, 72.
- ^ Stephanie W. Jamison & Joel P. Brereton 2014, p. 50.
- ^ Stephanie W. Jamison & Joel P. Brereton 2014, pp. 66–67.
- ^ Richard Gombrich (2006). Theravada Buddhism: A Social History from Ancient Benares to Modern Colombo. Routledge. pp. 24–25. ISBN 978-1-134-90352-8.
- ^ Gérard Huet; Amba Kulkarni; Peter Scharf (2009). Sanskrit Computational Linguistics: First and Second International Symposia Rocquencourt, France, October 29–31, 2007 Providence, RI, USA, May 15–17, 2008, Revised Selected Papers. Springer. pp. v–vi. ISBN 978-3-642-00154-3.
- ^ Cardona, George (1998), Pāṇini: A Survey of Research, Motilal Banarsidass, p. 268, ISBN 978-81-208-1494-3
- ^ The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica (2013). Ashtadhyayi, Work by Panini. Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 23 October 2017., Quote: "Ashtadhyayi, Sanskrit Aṣṭādhyāyī ("Eight Chapters"), Sanskrit treatise on grammar written in the 6th to 5th century BCE by the Indian grammarian Panini."
- ^ Frits Staal (1965), Euclid and Pāṇini, Philosophy East and West, Vol. 15, No. 2 (Apr., 1965), pp. 99–116
- ^ Harold G. Coward 1990, pp. 13–14, 111.
- ^ Pāṇini; Sumitra Mangesh Katre (1989). Aṣṭādhyāyī of Pāṇini. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. xix–xxi. ISBN 978-81-208-0521-7.
- ^ Harold G. Coward 1990, pp. 13-14, 111.
- ^ Louis Renou & Jean Filliozat. L'Inde Classique, manuel des etudes indiennes, vol.II pp.86–90, École française d'Extrême-Orient, 1953, reprinted 2000. ISBN 2-85539-903-3.
- ^ Angot, Michel. L'Inde Classique, pp.213–215. Les Belles Lettres, Paris, 2001. ISBN 2-251-41015-5
- ^ Yuji Kawaguchi; Makoto Minegishi; Wolfgang Viereck (2011). Corpus-based Analysis and Diachronic Linguistics. John Benjamins Publishing Company. pp. 223–224. ISBN 978-90-272-7215-7.
- ^ John Bowman (2005). Columbia Chronologies of Asian History and Culture. Columbia University Press. p. 728. ISBN 978-0-231-50004-3.
- ^ Richard Salomon (1998). Indian Epigraphy: A Guide to the Study of Inscriptions in Sanskrit, Prakrit, and the other Indo-Aryan Languages. Oxford University Press. p. 11. ISBN 978-0-19-535666-3.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Juhyung Rhi (2009). on the Peripheries of Civilizations: The Evolution of a Visual Tradition in Gandhāra". Journal of Central Eurasian Studies. 1: 5, 1–13.
- ^ Rita Sherma; Arvind Sharma (2008). Hermeneutics and Hindu Thought: Toward a Fusion of Horizons. Springer. p. 235. ISBN 978-1-4020-8192-7.
- ^ Falk, Harry (1993). Schrift im alten Indien: ein Forschungsbericht mit Anmerkungen (in German). Gunter Narr Verlag. pp. 109–167.
- ^ Salomon, Richard (1995). "Review: on the Origin of the Early Indian Scripts". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 115 (2): 271–278. doi:10.2307/604670. JSTOR 604670.
- ^ Scharfe, Hartmut (2002), Education in Ancient India, Handbook of Oriental Studies, Leiden, Netherlands: Brill, pp. 10–12
- ^ Oskar von Hinüber (1989). Der Beginn der Schrift und frühe Schriftlichkeit in Indien. Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur. pp. 241–245. OCLC 22195130.
- ^ Jack Goody (1987). The Interface Between the Written and the Oral. Cambridge University Press. pp. 110–124. ISBN 978-0-521-33794-6.
- ^ Johannes Bronkhorst (2002), Literacy and Rationality in Ancient India, Asiatische Studien / Études Asiatiques, 56(4), pages 803–804, 797–831
- ^ Louis Renou & Jagbans Kishore Balbir 2004, pp. 53.
- ^ Louis Renou & Jagbans Kishore Balbir 2004, pp. 53–54.
- ^ Thomas Burrow 2001, pp. 33–34.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e A. M. Ruppel 2017, pp. 378–383.
- ^ Arthur Anthony Macdonell (1997). A Sanskrit Grammar for Students. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 236–244. ISBN 978-81-208-0505-7.
- ^ Louis Renou & Jagbans Kishore Balbir 2004, pp. 1–59.
- ^ Fleet, John Faithfull (1907). Corpus Inscriptionum Indicarum Vol 3 (1970)ac 4616. p. 153, Line 14 of the inscription.
- ^ Anne Kessler-Persaud 2009, p. 3.
- ^ John L. Brockington 1998, p. 379.
- ^ Alfred C. Woolner (1986). Introduction to Prakrit. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 6, context: 1–10. ISBN 978-81-208-0189-9.
- ^ Clarence Maloney (1978). Language and Civilization Change in South Asia. Brill Academic. pp. 111–114. ISBN 978-90-04-05741-8.
- ^ Gaurinath Bhattacharyya Shastri (1987). A Concise History of Classical Sanskrit Literature. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 18–19. ISBN 978-81-208-0027-4.
- ^ Rune Edvin Anders Johansson (1981). Pali Buddhist Texts: Explained to the Beginner. Psychology Press. p. 7. ISBN 978-0-7007-1068-3., Quote: "Pali is known mainly as the language of Theravada Buddhism. [...] Very little is known about its origin. We do not know where it was spoken or if it originally was a spoken language at all. The ancient Ceylonese tradition says that the Buddha himself spoke Magadhi and that this language was identical to Pali."
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Paul Dundas (2003). The Jains. Routledge. pp. 69–70. ISBN 978-0-415-26606-2.
- ^ "Ethnologue report for language code: pli". Ethnologue. Retrieved 20 July 2018.
- ^ P.S. Krishnavarma (1881). Sanskrit as a living language in India: Journal of the National Indian Association. Henry S. King & Company. pp. 737–745.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Gaurinath Bhattacharyya Shastri (1987). A Concise History of Classical Sanskrit Literature. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 20–23. ISBN 978-81-208-0027-4.
- ^ Moriz Winternitz (1996). A History of Indian Literature. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 42–46. ISBN 978-81-208-0264-3.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d Deshpande 2011, pp. 222–223.
- ^ Etinne Lamotte (1976), Histoire du buddhisme indien, des origines à l'ère saka, Tijdschrift Voor Filosofie 21 (3):539–541, Louvain-la-Neuve: Université de Louvain, Institut orientaliste
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Sheldon Pollock (1996). Jan Houben (ed.). The Sanskrit Cosmopolis, A.D. 300–1300: Transculturation, Vernacularization, and the Question of Ideology, in "Ideology and status of Sanskrit: contributions to the history of the Sanskrit language". Leiden New York: E.J. Brill. pp. 197–199, for context and details, please see 197–239. ISBN 978-90-04-10613-0.
- ^ Gérard Huet; Amba Kulkarni; Peter Scharf (2009). Sanskrit Computational Linguistics. Springer. pp. v–vi. ISBN 978-3-642-00155-0.
- ^ P M Scharf; M Hyman (2009). V Govindaraju and S Setlur (ed.). Guide to OCR for Indic Scripts: Document Recognition and Retrieval. Springer. p. 238. ISBN 978-1-84800-330-9.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Justin McDaniel; Lynn Ransom (2015). From Mulberry Leaves to Silk Scrolls: New Approaches to the Study of Asian Manuscript Traditions. University of Pennsylvania Press. pp. 233–234. ISBN 978-0-8122-4736-7.
- ^ Gaurinath Bhattacharyya Shastri (1987). A Concise History of Classical Sanskrit Literature. Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 978-81-208-0027-4.
- ^ Banerji 1989, pp. 618-632, see also the extended list of Sanskrit texts in Part II.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d J.F. Staal (1976). Herman Parret (ed.). History of Linguistic Thought and Contemporary Linguistics. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 102–130. ISBN 978-3-11-005818-5.
- ^ Thomas Burrow 2001, pp. 57–64, 289, 319.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Madhav Deshpande (2010), Language and Testimony in Classical Indian Philosophy, Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy, Source Link
- ^ Stephanie Theodorou (2011), Bhartrihari (c. 450—510 C.E.), IEP, Source link
- ^ J.F. Staal (1976). Herman Parret (ed.). History of Linguistic Thought and Contemporary Linguistics. Walter de Gruyter. pp. 121–125. ISBN 978-3-11-005818-5.
- ^ Wayman 1965, pp. 111–115.
- ^ John Kelly (1996). Jan E. M. Houben (ed.). Ideology and Status of Sanskrit: Contributions to the History of the Sanskrit Language. BRILL Academic. pp. 87–102. ISBN 978-90-04-10613-0.
- ^ Louis Renou & Jagbans Kishore Balbir 2004, pp. =177-180.
- ^ Paul Dundas (2006). Patrick Olivelle (ed.). Between the Empires : Society in India 300 BCE to 400 CE. Oxford University Press. pp. 395–396. ISBN 978-0-19-977507-1.
- ^ K Preisendanz (2018). Florence Bretelle-Establet; Stéphane Schmitt (eds.). Pieces and Parts in Scientific Texts. Springer. pp. 175–178 with footnotes. ISBN 978-3-319-78467-0.
- ^ Eli Franco (2004), The Spitzer Manuscript: The Oldest Philosophical Manuscript in Sanskrit, Volume 1 & 2, Verlag Der Österreichischen Akademie Der Wissenschaften (Austrian Academy of Sciences Press), ISBN 978-37001-3-3018, pages 461–465
- ^ Eli Franco (2003). "The Oldest Philosophical Manuscript in Sanskrit". Journal of Indian Philosophy. 31 (1/3): 21–31. doi:10.1023/A:1024690001755. JSTOR 23497034.
- ^ Robert E. Buswell Jr. & Donald S. Lopez Jr. 2013, p. 504.
- ^ Stephen K. Stein (2017). The Sea in World History: Exploration, Travel, and Trade [2 volumes]. ABC-CLIO. p. 147. ISBN 978-1-4408-3551-3.
- ^ Charles Taliaferro (2010). A Dictionary of Philosophy of Religion. Bloomsbury Publishing. pp. 245–246. ISBN 978-1-4411-8504-4.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Michael C. Howard 2012, p. 21.
- ^ Dalai Lama 1979, pp. 3–5.
- ^ Colin P. Masica 1993, pp. 55–56.
- ^ Keat Gin Ooi (2004). Southeast Asia: A Historical Encyclopedia, from Angkor Wat to East Timor. ABC-CLIO. p. 643. ISBN 978-1-57607-770-2.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Thomas Burrow 2001, p. 60.
- ^ Houben, Jan (1996). Ideology and status of Sanskrit: contributions to the history of the Sanskrit language. Leiden New York: E.J. Brill. p. 11. ISBN 978-90-04-10613-0.
- ^ Hock, Hans Henrich (1983). Kachru, Braj B (ed.). "Language-death phenomena in Sanskrit: grammatical evidence for attrition in contemporary spoken Sanskrit". Studies in the Linguistic Sciences. 13:2.
- ^ Sheldon Pollock 2009, pp. 167–168.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d Hanneder, J. (2002). on "The Death of Sanskrit"". Indo-Iranian Journal. 45 (4): 293–310. doi:10.1023/a:1021366131934.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e Pollock, Sheldon (2001). "The Death of Sanskrit". Comparative Studies in Society and History. 43 (2): 392–426. doi:10.1017/s001041750100353x.
- ^ Audrey Truschke (2016). Culture of Encounters: Sanskrit at the Mughal Court. Columbia University Press. pp. 9–15, 30–36, 45–47. ISBN 978-0-231-54097-1.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Madhav M. Deshpande (1993). Sanskrit & Prakrit, Sociolinguistic Issues. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 118–124. ISBN 978-81-208-1136-2.
- ^ B. B. Kachru (1981). Kashmiri Literature. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. pp. 24–25. ISBN 978-3-447-02129-6.
- ^ Gurnam Singh Sidhu Brard (2007). East of Indus. Hemkunt Press. pp. 80–82. ISBN 978-81-7010-360-8.
- ^ John Snelling (1991). The Buddhist Handbook. Inner Traditions. pp. vi, 1. ISBN 978-0-89281-319-3.
- ^ M. Ramakrishnan Nair (1974). Sanskrit Family: A Comparative Study of Indian & European Languages as a Whole. Ramakrishnan Nair. p. 5.
- ^ Hatcher, B. A. (2007). "Sanskrit and the morning after: The metaphorics and theory of intellectual change". Indian Economic. 44 (3): 333–361. doi:10.1177/001946460704400303.
- ^ Moriz Winternitz (1996). A History of Indian Literature, Volume 1. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 37–39. ISBN 978-81-208-0264-3.
- ^ Hatcher, Brian A. (2016). "Sanskrit and the morning after". The Indian Economic & Social History Review. 44 (3): 333–361. doi:10.1177/001946460704400303. ISSN 0019-4646.
- ^ Hanneder, J. (2009), "Modernes Sanskrit: eine vergessene Literatur", in Straube, Martin; Steiner, Roland; Soni, Jayandra; Hahn, Michael; Demoto, Mitsuyo (eds.), Pāsādikadānaṃ: Festschrift für Bhikkhu Pāsādika, Indica et Tibetica Verlag, pp. 205–228
- ^ Robert P. Goldman & Sally J Sutherland Goldman 2002, pp. xi–xii.
- ^ Seth, Sanjay (2007). Subject lessons: the Western education of colonial India. Durham, NC: Duke University Press. pp. 172–176. ISBN 978-0-8223-4105-5.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e Colin P. Masica 1993, pp. 50–57.
- ^ Philipp Strazny (2013). Encyclopedia of Linguistics. Routledge. pp. 499–500. ISBN 978-1-135-45522-4.
- ^ Sagarika Dutt (2014). India in a Globalized World. Oxford University Press. pp. 16–17. ISBN 978-0-7190-6901-7.
- ^ Cynthia Groff (2017). The Ecology of Language in Multilingual India. Palgrave Macmillan. pp. 183–185. ISBN 978-1-137-51961-0.
- ^ Burjor Avari (2016). India: The Ancient Past: A History of the Indian Subcontinent from c. 7000 BCE to CE 1200. Routledge. pp. 66–67. ISBN 978-1-317-23673-3.
- ^ Sheldon Pollock (1996). Jan E. M. Houben (ed.). Ideology and Status of Sanskrit. BRILL Academic. pp. 197–223 with footnotes. ISBN 978-90-04-10613-0.
- ^ William S.-Y. Wang; Chaofen Sun (2015). The Oxford Handbook of Chinese Linguistics. Oxford University Press. pp. 6–19, 203–212, 236–245. ISBN 978-0-19-985633-6.
- ^ Thomas Burrow 2001, pp. 63-66.
- ^ Jinah Kim (2013). Receptacle of the Sacred: Illustrated Manuscripts and the Buddhist Book Cult in South Asia. University of California Press. pp. 8, 13–15, 49. ISBN 978-0-520-27386-3.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Pieter C. Verhagen (1994). A History of Sanskrit Grammatical Literature in Tibet. BRILL. pp. 159–160. ISBN 978-90-04-09839-8.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 154-155.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 158-159.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 155-157.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Salomon 1998, p. 158.
- ^ Salomon 1998, p. 157.
- ^ Salomon 1998, p. 155.
- ^ William M. Johnston (2013). Encyclopedia of Monasticism. Routledge. p. 926. ISBN 978-1-136-78716-4.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Todd T. Lewis; Subarna Man Tuladhar (2009). Sugata Saurabha An Epic Poem from Nepal on the Life of the Buddha by Chittadhar Hridaya. Oxford University Press. pp. 343–344. ISBN 978-0-19-988775-0.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 159-160.
- ^ Patrick Olivelle (2006). Between the Empires: Society in India 300 BCE to 400 CE. Oxford University Press. p. 356. ISBN 978-0-19-977507-1.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 152-153.
- ^ Rewi Alley (1957). Journey to Outer Mongolia: a diary with poems. Caxton Press. pp. 27–28.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Salomon 1998, pp. 153–154.
- ^ Gian Luca Bonora; Niccolò Pianciola; Paolo Sartori (2009). Kazakhstan: Religions and Society in the History of Central Eurasia. U. Allemandi. pp. 65, 140. ISBN 978-88-42217-558.
- ^ Bjarke Frellesvig (2010). A History of the Japanese Language. Cambridge University Press. pp. 164–165, 183. ISBN 978-1-139-48880-8.
- ^ Donald S. Lopez Jr. (2017). Hyecho's Journey: The World of Buddhism. University of Chicago Press. pp. 16–22, 33–42. ISBN 978-0-226-51806-0.
- ^ Salomon 1998, p. 160 with footnote 134.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Cynthia Groff (2013). Jo Arthur Shoba and Feliciano Chimbutane (ed.). Bilingual Education and Language Policy in the Global South. Routledge. p. 178. ISBN 978-1-135-06885-1.
- ^ "Sanskrit second official language of Uttarakhand". The Hindu. 21 January 2010. ISSN 0971-751X. Retrieved 2 October 2018.
- ^ "HP Assy clears three Bills, Sanskrit becomes second official language".
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e Jamison 2008, pp. 8–9.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Jamison 2008, p. 9.
- ^ Robert P. Goldman & Sally J Sutherland Goldman 2002, pp. 1–9.
- ^ Michael Coulson, Richard Gombrich & James Benson 2011, pp. 21–36.
- ^ Colin P. Masica 1993, pp. 163–165.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Robert P. Goldman & Sally J Sutherland Goldman 2002, pp. 13–19.
- ^ ḹ is not an actual sound of Sanskrit, but rather a graphic convention included among the written vowels to maintain the symmetry of short–long pairs of letters. (Salomon 2003 p.75)
- ^ Colin P. Masica 1993, p. 146 notes of this diacritic that "there is some controversy as to whether it represents a homorganic nasal stop [...], a nasalised vowel, a nasalised semivowel, or all these according to context".
- ^ This visarga is a consonant, not a vowel. It's a post-vocalic voiceless glottal fricative [h], and an allophone of s (or less commonly r) usually in word-final position. Some traditions of recitation append an echo of the preceding vowel after the [h] (Wikner 1996, p. 6): इः [ihi]. Colin P. Masica 1993, p. 146 considers the visarga, along with letters ङ ṅa and ञ ña, for the "largely predictable" velar and palatal nasals, to be examples of "phonetic overkill in the [writing] system".
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Colin P. Masica 1993, pp. 160–161.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d Jamison 2008, pp. 9–10.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Jamison 2008, p. 10.
- ^ A. M. Ruppel 2017, pp. 18–19.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Jamison 2008, pp. 10–11.
- ^ Jamison 2008, p. 11.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Jamison 2008, pp. 11–12.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Jamison 2008, p. 12.
- ^ Colin P. Masica 1993, pp. 164–166.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d Jamison 2008, p. 13.
- ^ Colin P. Masica 1993, pp. 163–164.
- ^ Jamison 2008, pp. 13–14.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e f Jamison 2008, p. 15.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e Jamison 2008, pp. 15–16.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d Jamison 2008, p. 20.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c A. M. Ruppel (2017). The Cambridge Introduction to Sanskrit. Cambridge University Press. pp. 31–33. ISBN 978-1-107-08828-3.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e A. M. Ruppel (2017). The Cambridge Introduction to Sanskrit. Cambridge University Press. pp. 33–34. ISBN 978-1-107-08828-3.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e Jamison 2008, pp. 19–20.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d e f g h Jamison 2008, pp. 16–17.
- ^ Jamison 2008, pp. 17–18.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Paul Kiparsky (2014). E.F.K. Koerner and R.E. Asher (ed.). Concise History of the Language Sciences: From the Sumerians to the Cognitivists. Elsevier. pp. 59–65. ISBN 978-1-4832-9754-5.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Jamison 2008, p. 21.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Jamison 2008, pp. 20–21.
- ^ Robert P. Goldman & Sally J Sutherland Goldman 2002, pp. 59, 79, 91, 113.
- ^ Thomas Burrow 2001, pp. 191–194.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b James Lochtefeld (2002), "Chandas" in The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Hinduism, Vol. 1: A-M, Rosen Publishing, ISBN 0-8239-2287-1, page 140
- ^ Moriz Winternitz (1988). A History of Indian Literature: Buddhist literature and Jaina literature. Motilal Banarsidass. p. 577. ISBN 978-81-208-0265-0.
- ^ Annette Wilke & Oliver Moebus 2011, pp. 391-392 with footnotes.
- ^ Annette Wilke & Oliver Moebus 2011, pp. 391–392 with footnotes.
- ^ Thomas Egenes (1996). Introduction to Sanskrit. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 86–91. ISBN 978-81-208-1693-0.
- ^ Winthrop Sargeant (2010). Christopher Key Chapple (ed.). The Bhagavad Gita: Twenty-fifth–Anniversary Edition. State University of New York Press. pp. 3–8. ISBN 978-1-4384-2840-6.
- ^ J. L. Brockington (1998). The Sanskrit Epics. BRILL Academic. pp. 117–130. ISBN 978-90-04-10260-6.
- ^ Peter Scharf (2013). Keith Allan (ed.). The Oxford Handbook of the History of Linguistics. Oxford University Press. pp. 228–234. ISBN 978-0-19-164344-6.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Alex Preminger; Frank J. Warnke; O. B. Hardison Jr. (2015). Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics. Princeton University Press. pp. 394–395. ISBN 978-1-4008-7293-0.
- ^ Har Dutt Sharma (1951). "Suvrttatilaka". Poona Orientalist: A Quarterly Journal Devoted to Oriental Studies. XVII: 84.
- ^ Patrick Olivelle (1998). The Early Upanisads : Annotated Text and Translation. Oxford University Press. pp. xvi–xviii, xxxvii. ISBN 978-0-19-535242-9.
- ^ Patrick Olivelle (2008). Collected Essays: Language, Texts and Society. Firenze University Press. pp. 293–295. ISBN 978-88-8453-729-4.
- ^ Maurice Winternitz 1963, pp. 3–4 with footnotes.
- ^ Patrick Olivelle (2008). Collected Essays: Language, Texts and Society. Firenze University Press. pp. 264–265. ISBN 978-88-8453-729-4.
- ^ Alf Hiltebeitel (2000), Review: John Brockington, The Sanskrit Epics, Indo-Iranian Journal, Volume 43, Issue 2, pages 161-169
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d Tatyana J. Elizarenkova (1995). Language and Style of the Vedic Rsis. State University of New York Press. pp. 111–121. ISBN 978-0-7914-1668-6.
- ^ Salomon 1998, p. 10.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 7–10, 86.
- ^ Jack Goody (1987). The Interface Between the Written and the Oral. Cambridge University Press. pp. 110–121. ISBN 978-0-521-33794-6.
- ^ Donald S. Lopez Jr. 1995, pp. 21–47
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Salomon 1998, p. 11.
- ^ Rita Sherma; Arvind Sharma (2008). Hermeneutics and Hindu Thought: Toward a Fusion of Horizons. Springer. p. 235. ISBN 978-1-4020-8192-7.;
Takao Hayashi (2008). Gavin Flood (ed.). The Blackwell Companion to Hinduism. John Wiley & Sons. p. 365. ISBN 978-0-470-99868-7. - ^ Lopon Nado (1982), The Development of Language in Bhutan, The Journal of the International Association of Buddhist Studies, Volume 5, Number 2, page 95, Quote: "Under different teachers, such as the Brahmin Lipikara and Deva Vidyasinha, he mastered Indian philology and scripts. According to Lalitavistara, there were as many as sixty-four scripts in India."
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 8–9 with footnotes.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 8–9.
- ^ Salomon 1998.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Salomon 1998, pp. 8–14.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 11–12.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Peter T. Daniels 1996, pp. 371–372.
- ^ Peter T. Daniels 1996, pp. 373–374, 376–378.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d Salomon 1998, pp. 14–16.
- ^ Peter T. Daniels 1996, pp. 373–375.
- ^ Peter T. Daniels 1996, pp. 373–376.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Peter T. Daniels 1996, pp. 373–374.
- ^ Charles Higham (2014). Encyclopedia of Ancient Asian Civilizations. Infobase Publishing. p. 294. ISBN 978-1-4381-0996-1.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 14-16.
- ^ Peter T. Daniels 1996, pp. 376–380.
- ^ Dhanesh Jain & George Cardona 2007, pp. 69–70 in Chapter 3 by Salomon.
- ^ Dhanesh Jain & George Cardona 2007, pp. 68–72 in Chapter 3 by Salomon, Quote: "Sanskrit and the Prakrits, at different times and places were written in a vast number of forms and derivatives of Brahmi. In the premodern period, in other words, these languages would be written by a given scribe in whatever happened to be the current local script [...]" – Richard Salomon, page 70.
- ^ Dhanesh Jain & George Cardona 2007, p. 72 in Chapter 3 by Salomon.
- ^ Bahadur Chand Chhabra (1970). "Sugh Terracotta with Brahmi Barakhadi". Bull. National Mus. (2): 14–16.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Dhanesh Jain & George Cardona 2007, pp. 68–70 in Chapter 3 by Salomon.
- ^ Nandanagiri Unicode Standards
- ^ Kathleen Kuiper (2010), The Culture of India, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, ISBN 978-1615301492, page 83
- ^ Richard Salomon (2014), Indian Epigraphy, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0195356663, pages 33–47
- ^ Sures Chandra Banerji (1989). A Companion to Sanskrit Literature. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 671–672. ISBN 978-81-208-0063-2.
- ^ Dhanesh Jain & George Cardona 2007, pp. 70, 75-77 in Chapter 3 by Salomon.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Dhanesh Jain & George Cardona 2007, pp. 75–77 in Chapter 3 by Salomon.
- ^ John Norman Miksic; Goh Geok Yian (2016). Ancient Southeast Asia. Taylor & Francis. p. 178. ISBN 978-1-317-27904-4.
- ^ Dhanesh Jain & George Cardona 2007, pp. 70–78 in Chapter 3 by Salomon.
- ^ Dhanesh Jain & George Cardona 2007, pp. 70–71, 75–76 in Chapter 3 by Salomon.
- ^ Dhanesh Jain & George Cardona 2007, pp. 70–71 in Chapter 3 by Salomon.
- ^ Dhanesh Jain & George Cardona 2007, pp. 72–73 in Chapter 3 by Salomon.
- ^ "Modern Transcription of Sanskrit". autodidactus.org.
- ^ Jan Gonda (2016). Visnuism and Sivaism: A Comparison. Bloomsbury Academic. pp. 166 note 243. ISBN 978-1-4742-8082-2.
- ^ James Hegarty (2013). Religion, Narrative and Public Imagination in South Asia: Past and Place in the Sanskrit Mahabharata. Routledge. pp. 46 note 118. ISBN 978-1-136-64589-1.
- ^ Theo Damsteegt (1978). Epigraphical Hybrid Sanskrit. Brill Academic. pp. 209–211.
- ^ Sonya Rhie Quintanilla (2007). History of Early Stone Sculpture at Mathura: Ca. 150 BCE – 100 CE. BRILL Academic. pp. 254–255. ISBN 978-90-04-15537-4.
- ^ Salomon 1998, p. 87 with footnotes.
- ^ Salomon 1998, p. 93.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Salomon 1998, pp. 87–88.
- ^ Sonya Rhie Quintanilla (2007). History of Early Stone Sculpture at Mathura: Ca. 150 BCE – 100 CE. BRILL Academic. pp. 260–263. ISBN 978-90-04-15537-4.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 87-88.
- ^ Sonya Rhie Quintanilla (2007). History of Early Stone Sculpture at Mathura: Ca. 150 BCE – 100 CE. BRILL Academic. p. 260. ISBN 978-90-04-15537-4.
- ^ Salomon 1998, p. 88.
- ^ Inscription No21 in Janert, l (1961). Mathura Inscriptions.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 88–89.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Salomon 1998, pp. 89–90.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c Salomon 1998, p. 89.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 10, 86–90
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Salomon 1998, pp. 91–94.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 90–91.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 90–91 with footnote 51.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 91–93.
- ^ Salomon 1998, p. 92, Quote: "Finally, after this transitional period in the fourth and early fifth centuries AD, Prakrit fell out of use completely in southern Indian inscriptions. For the next few centuries Sanskrit was the sole epigraphic language, until the regional Dravidian languages began to come into use around the seventh century"..
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Salomon 1998, p. 92.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Salomon 1998, pp. 92–93.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 110–112, 132–148.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 110–126.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 126–132.
- ^ Salomon 1998, pp. 148–149.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Salomon 1998, pp. 149–150.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Peter T. Daniels 1996, pp. 445–447 in the chapter by Christopher Court.
- ^ Peter T. Daniels 1996, pp. 445–456 in the chapter by Christopher Court.
- ^ Peter T. Daniels 1996, pp. 446–448 in the chapter by Christopher Court.
- ^ Colin P. Masica 1993, pp. 137–144.
- ^ Mahadevan 2003.
- ^ Banerji 1989, p. 672 with footnotes.
- ^ Jan Gonda (1975), Vedic literature (Saṃhitās and Brāhmaṇas), Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 3-447-01603-5
- ^ Teun Goudriaan, Hindu Tantric and Śākta Literature, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 3-447-02091-1
- ^ Dhanesh Jain & George Cardona 2007.
- ^ Hartmut Scharfe, A history of Indian literature. Vol. 5, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 3-447-01722-8
- ^ J Duncan M Derrett (1978), Dharmasastra and Juridical Literature: A history of Indian literature (Editor: Jan Gonda), Vol. 4, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 3-447-01519-5
- ^ Patrick Olivelle, King, Governance, and Law in Ancient India, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-989182-5
- ^ Kim Plofker (2009), Mathematics in India, Princeton University Press, ISBN 978-0-691-12067-6
- ^ David Pingree, A Census of the Exact Sciences in Sanskrit, Volumes 1 to 5, American Philosophical Society, ISBN 978-0-87169-213-9
- ^ MS Valiathan, The Legacy of Caraka, Orient Blackswan, ISBN 978-81-250-2505-4
- ^ Kenneth Zysk, Medicine in the Veda, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 978-81-208-1401-1
- ^ JJ Meyer, Sexual Life in Ancient India, Vol 1 and 2, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-1-4826-1588-3
- ^ John L. Brockington 1998.
- ^ Sures Chandra Banerji (1989). A Companion to Sanskrit Literature: Spanning a Period of Over Three Thousand Years, Containing Brief Accounts of Authors, Works, Characters, Technical Terms, Geographical Names, Myths, Legends and Several Appendices. Motilal Banarsidass. pp. 1–4, with a long list in Part II. ISBN 978-81-208-0063-2.
- ^ Ludwik Sternbach (1974), Subhāṣita: Gnomic and Didactic Literature, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 978-3-447-01546-2
- ^ The Sanskrit Drama, Oxford University Press
- ^ Rachel Baumer and James Brandon (1993), Sanskrit Drama in Performance, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 81-208-0772-3
- ^ Mohan Khokar (1981), Traditions of Indian Classical Dance, Peter Owen Publishers, ISBN 978-0-7206-0574-7
- ^ Emmie te Nijenhuis, Musicological literature (A History of Indian literature ; v. 6 : Scientific and technical literature ; Fasc. 1), Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 978-3-447-01831-9
- ^ Lewis Rowell, Music and Musical Thought in Early India, University of Chicago Press, ISBN 0-226-73033-6
- ^ Edwin Gerow, A history of Indian literature. Vol. 5, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 3-447-01722-8
- ^ Ludo Rocher (1986), The Puranas, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 978-3-447-02522-5
- ^ Karl Potter, The Encyclopedia of Indian Philosophies, Volumes 1 through 27, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 81-208-0309-4
- ^ Gyula Wojtilla (2006), History of Kr̥ṣiśāstra, Otto Harrassowitz Verlag, ISBN 978-3-447-05306-8
- ^ PK Acharya (1946), An Encyclopedia of Hindu Architecture, Oxford University Press, Also see Volumes 1 to 6
- ^ Bruno Dagens (1995), Mayamata : An Indian Treatise on Housing Architecture and Iconography, ISBN 978-81-208-3525-2
- ^ Stella Kramrisch, Hindu Temple, Vol. 1 and 2, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 978-81-208-0222-3
- ^ Rajbali Pandey (2013), Hindu Saṁskāras: Socio-religious Study of the Hindu Sacraments, 2nd Edition, Motilal Banarsidass, ISBN 978-8120803961
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Banerji 1989, p. 634-635 with the list in Appendix IX.
- ^ Eltschinger 2017.
- ^ Wayman 1965.
- ^ Paul Dundas (2003). The Jains. Routledge. pp. 68–76, 149, 307–310. ISBN 978-1-134-50165-6.
- ^ Wendy Doniger (1993). Purana Perennis: Reciprocity and Transformation in Hindu and Jaina Texts. State University of New York Press. pp. 192–193. ISBN 978-0-7914-1381-4.
- ^ Oberlies, Thomas (2003). A Grammar of Epic Sanskrit. Berlin New York: Walter de Gruyter. pp. xxvii–xxix. ISBN 978-3-11-014448-2.
- ^ Edgerton, Franklin (2004). Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit grammar and dictionary. Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 978-81-215-1110-0.
- ^ Staal 1963, pp. 261.
- ^ Rao, Velcheru (2002). Classical Telugu poetry an anthology. Berkeley, Calif: University of California Press. p. 3. ISBN 978-0-520-22598-5.
- ^ Sugam Marathi Vyakaran & Lekhana. 2007. Nitin publications. Author: M.R.Walimbe
- ^ Carey, William (1805). A Grammar of the Marathi Language. Serampur [sic]: Serampore Mission Press. ISBN 9781108056311.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b c d William S.-Y. Wang; Chaofen Sun (2015). The Oxford Handbook of Chinese Linguistics. Oxford University Press. pp. 5–6, 12, 236–247. ISBN 978-0-19-985633-6., Quote: "In chapter 18, Shi Xiangdong makes it clear that the influence of Buddhist Sanskrit on the Chinese language has been considerable. Many words have crossed the line from religious discourse to everyday use."
- ^ Charles Orzech; Henrik Sørensen; Richard Payne (2011). Esoteric Buddhism and the Tantras in East Asia. BRILL Academic. pp. 985–996. ISBN 978-90-04-18491-6.
- ^ William S.-Y. Wang; Chaofen Sun (2015). The Oxford Handbook of Chinese Linguistics. Oxford University Press. pp. 5–6. ISBN 978-0-19-985633-6.
- ^ Gulik, R. H. (2001). Siddham: an essay on the history of Sanskrit studies in China and Japan. New Delhi: International Academy of Indian Culture and Aditya Prakashan. pp. 5–133. ISBN 978-81-7742-038-8.
- ^ Zoetmulder, P. J. (1982). Old Javanese-English Dictionary.
- ^ Joshi, Manoj. Passport India 3rd Ed., eBook. World Trade Press. p. 15.
- ^ "Nichiren Buddhism Library". www.nichirenlibrary.org. Archived from the original on 22 February 2015.
- ^ Orzech, Charles; Sørensen, Henrik; Payne, Richard (2011). Esoteric Buddhism and the Tantras in East Asia. BRILL. p. 985. ISBN 978-9004184916.
- ^ Paul Dundas (1996). Jan E. M. Houben (ed.). Ideology and Status of Sanskrit: Contributions to the History of the Sanskrit Language. BRILL. pp. 152–155. ISBN 978-90-04-10613-0.
- ^ Swami Veda Bharati (1968). Ritual songs and folksongs of the Hindus of Surinam: proefschrift. Brill Archive. pp. 11–22. GGKEY:GJ0YGRH08YW.
- ^ John Stratton Hawley (1996). Devi: Goddesses of India. University of California Press. pp. 42–44. ISBN 978-0-520-20058-6.
- ^ John Stratton Hawley (1996). Devi: Goddesses of India. University of California Press. pp. 187–188. ISBN 978-0-520-20058-6.
- ^ Christopher John Fuller (2003). The Renewal of the Priesthood: Modernity and Traditionalism in a South Indian Temple. Princeton University Press. pp. 49–53. ISBN 978-0-691-11658-7.
- ^ Richard H. Davis (2014). The Bhagavad Gita: A Biography. Princeton University Press. p. 179. ISBN 978-1-4008-5197-3.
- ^ Prajapati, Manibhai (2005). Post-independence Sanskrit literature: a critical survey (1 ed.). New Delhi: Standard publishers India.
- ^ Ranganath, S (2009). Modern Sanskrit Writings in Karnataka (PDF) (1st ed.). New Delhi: Rashtriya Sanskrit Sansthan. p. 7. ISBN 978-81-86111-21-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 1 May 2012. Retrieved 28 October 2014.:
Contrary to popular belief, there is an astonishing quality of creative upsurge of writing in Sanskrit today. Modern Sanskrit writing is qualitatively of such high order that it can easily be treated on par with the best of Classical Sanskrit literature, It can also easily compete with the writings in other Indian languages.
- ^ "Adhunika Sanskrit Sahitya Pustakalaya". Rashtriya Sanskrit Sansthan. Archived from the original on 13 January 2013. Retrieved 28 October 2014.:
The latter half of the nineteenth century marks the beginning of a new era in Sanskrit literature. Many of the modern Sanskrit writings are qualitatively of such high order that they can easily be treated at par with the best of classical Sanskrit works, and they can also be judged in contrast to the contemporary literature in other languages.
- ^ "Sanskrit's first Jnanpith winner is a 'poet by instinct'". The Indian Express. 14 January 2009.
- ^ "Samveda". Retrieved 5 May 2015.
- ^ "Awards for World Music 2008". BBC.
- ^ Haspelmath, Martin (2009). Loanwords in the World's Languages: A Comparative Handbook. De Gruyter Mouton. p. 724. ISBN 978-3110218435.
- ^ Jose G. Kuizon (1964). "The Sanskrit Loan-words in the Cebuano-Bisayan Language". Asian Folklore Studies. 23 (1): 111–158. doi:10.2307/1177640. JSTOR 1177640.
- ^ Sak-Humphry, Channy. The Syntax of Nouns and Noun Phrases in Dated Pre-Angkorian Inscriptions. Mon Khmer Studies 22: 1–26.
- ^ 위로 점프: a b Mayank Austen Soofi (23 November 2012). "Delhi's Belly | Sanskrit-vanskrit". Livemint. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- ^ "News on Air". News on Air. 15 August 2012. Archived from the original on 5 September 2012. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- ^ "News archive search". Newsonair. 15 August 2012. Archived from the original on 15 January 2013. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- ^ "Doordarshan News Live webcast". Webcast.gov.in. Retrieved 6 December 2012.
- ^ "Comparative speaker's strength of scheduled languages − 1971, 1981, 1991 and 2001". Census of India, 2001. Office of the Registrar and Census Commissioner, India. Archived from the original on 11 April 2009. Retrieved 31 December 2009.
- ^ 10,000 More Sanskrit Speakers in India in 2011 Census, News18 India, 15 July 2018
- ^ "This village speaks gods language – India – The Times of India". The Times of India. 13 August 2005. Retrieved 5 April 2012.
- ^ Ghosh, Aditya (20 September 2008). "Sanskrit boulevard". Hindustan Times. Retrieved 5 April 2012.
- ^ Bhaskar, B.V.S. (31 July 2009). "Mark of Sanskrit". The Hindu.
- ^ "Orissa's Sasana village – home to Sanskrit pundits! !". The India Post. 9 April 2010. Retrieved 5 April 2012.
- ^ "In 2013, UPA to CBSE: Make Sanskrit a must". The Indian Express. 4 December 2014.
- ^ "Sanskrit @ St James". Sanskrit @ St James. Retrieved 8 October 2017.
- ^ Varija Yelagalawadi. "Why SAFL?". Samskrita Bharati USA. Archived from the original on 12 May 2015.
- ^ Sydney Grammar School. "Headmaster's Introduction". Archived from the original on 15 March 2015.
- ^ "Home". John Scottus School. Retrieved 24 May 2019.
- ^ "Sanskrit script opens the path to spirituality and helps improve focus | Saturday Star". www.iol.co.za. Retrieved 24 May 2019.
- ^ Barrett, David V. (1996). Sects, cults, and alternative religions : a world survey and sourcebook. London: Blandford. ISBN 0713725672. OCLC 36909325.
- ^ Friedrich Max Müller (1859). A History of Ancient Sanskrit Literature So Far as it Illustrates the Primitive Religion of the Brahmans. Williams and Norgate. p. 1.
- ^ Thomas R. Trautmann (2004). Aryans and British India. Yoda Press. pp. 73–84, 62–87. ISBN 978-81-902272-1-6.
- ^ Thomas R. Trautmann (2004). Aryans and British India. Yoda Press. pp. 96–97. ISBN 978-81-902272-1-6.
- ^ Thomas R. Trautmann (2004). Aryans and British India. Yoda Press. pp. 124–126. ISBN 978-81-902272-1-6.
- ^ Thomas R. Trautmann (2004). Aryans and British India. Yoda Press. pp. 133–142. ISBN 978-81-902272-1-6.
- ^ Upadhyay, Pankaj; Jaiswal, Umesh Chandra; Ashish, Kumar (2014). "TranSish: Translator from Sanskrit to English-A Rule based Machine Translation". International Journal of Current Engineering and Technology: 2277–4106.
- ^ TNI Angkatan Darat. Official website of the Indonesian Army.
- ^ Akademi Militer. Official website of the Indonesian Military Academy.
- ^ Sejarah. Official website of the Air-Force Special Forces (Paskhas).
- ^ Korps Marinir. Official website of the Indonesian Marine Corps.
- ^ Vibhuti Patel (18 December 2011). "Gandhi as operatic hero". The Hindu.
- ^ Rahim, Sameer (4 December 2013). "The opera novice: Satyagraha by Philip Glass". Telegraph. london.
- ^ Morgan, Les (2011). Croaking frogs: a guide to Sanskrit metrics and figures of speech. Los Angeles: Mahodara Press. p. 1. ISBN 978-1-4637-2562-4.
- ^ Doval, Nikita (24 June 2013). "Classic conversations". The Week. Archived from the original on 31 October 2014.
- ^ "Yoga and Music". Yoga Journal.
- ^ "Indiana Jones and the Temple of Doom (John Williams)". Filmtracks. 11 November 2008. Retrieved 5 April 2012.
- ^ "Episode I FAQ". Star Wars Faq. Archived from the original on 11 October 2003.
- ^ "Battlestar Galactica (TV Series 2004–2009)". IMDb.
- ^ "The Child In Us Lyrics – Enigma". Lyricsfreak.com. Retrieved 27 January 2013.
Bibliography[edit]
- H. W. Bailey (1955). "Buddhist Sanskrit". The Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society of Great Britain and Ireland. Cambridge University Press. 87 (1/2): 13–24. doi:10.1017/S0035869X00106975. JSTOR 25581326.
- Banerji, Sures (1989). A companion to Sanskrit literature: spanning a period of over three thousand years, containing brief accounts of authors, works, characters, technical terms, geographical names, myths, legends, and several appendices. Delhi: Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 978-81-208-0063-2.
- Guy L. Beck (1995). Sonic Theology: Hinduism and Sacred Sound. Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 978-81-208-1261-1.
- Guy L. Beck (2006). Sacred Sound: Experiencing Music in World Religions. Wilfrid Laurier Univ. Press. ISBN 978-0-88920-421-8.
- Robert S.P. Beekes (2011). Comparative Indo-European Linguistics: An introduction, 2nd edition. John Benjamins Publishing. ISBN 978-90-272-8500-3.
- Benware, Wilbur (1974). The Study of Indo-European Vocalism in the 19th Century: From the Beginnings to Whitney and Scherer: A Critical-Historical Account. Benjamins. ISBN 978-90-272-0894-1.
- Shlomo Biderman (2008). Crossing Horizons: World, Self, and Language in Indian and Western Thought. Columbia University Press. ISBN 978-0-231-51159-9.
- Claire Bowern; Bethwyn Evans (2015). The Routledge Handbook of Historical Linguistics. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-74324-8.
- John L. Brockington (1998). The Sanskrit Epics. BRILL Academic. ISBN 978-90-04-10260-6.
- Johannes Bronkhorst (1993). "Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit: The Original Language". Aspects of Buddhist Sanskrit: Proceedings of the International Symposium on the Language of Sanskrit Buddhist Texts, Oct. 1-5, 1991. Sarnath. pp. 396–423. ISBN 978-81-900149-1-5.
- Bryant, Edwin (2001). The Quest for the Origins of Vedic Culture: The Indo-Aryan Migration Debate. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-513777-4.
- Edwin Francis Bryant; Laurie L. Patton (2005). The Indo-Aryan Controversy: Evidence and Inference in Indian History. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-7007-1463-6.
- Thomas Burrow (2001). The Sanskrit Language. Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 978-81-208-1767-8.
- Robert E. Buswell Jr.; Donald S. Lopez Jr. (2013). The Princeton Dictionary of Buddhism. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-1-4008-4805-8.
- George Cardona (2012). Sanskrit Language. Encyclopaedia Britannica.
- James Clackson (18 October 2007). Indo-European Linguistics: An Introduction. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-139-46734-6.
- Coulson, Michael (1992). Sanskrit : an introduction to the classical language, 2nd Edition as revised by Richard Gombrich and James Benson. Random House. ISBN 978-0-340-56867-5. OCLC 26550827.
- Michael Coulson; Richard Gombrich; James Benson (2011). Complete Sanskrit: A Teach Yourself Guide. Mcgraw-Hill. ISBN 978-0-07-175266-4.
- Harold G. Coward (1990). The Philosophy of the Grammarians, in Encyclopedia of Indian Philosophies Volume 5 (Editor: Karl Potter). Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-81-208-0426-5.
- Suniti Kumar Chatterji (1957). "Indianism and Sanskrit". Annals of the Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute. Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute. 38 (1/2): 1–33. JSTOR 44082791.
- Peter T. Daniels (1996). The World's Writing Systems. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-507993-7.
- Deshpande, Madhav (2011), "Efforts to Vernacularize Sanskrit: Degree of Success and Failure", in Joshua Fishman, Ofelia Garcia (ed.), Handbook of Language and Ethnic Identity: The Success-Failure Continuum in Language and Ethnic Identity Efforts, 2, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-983799-1
- Will Durant (1963). Our oriental heritage. Simon & Schuster. ISBN 978-1567310122.
- Eltschinger, Vincent (2017). "Why Did the Buddhists Adopt Sanskrit?". Open Linguistics. 3 (1). doi:10.1515/opli-2017-0015. ISSN 2300-9969.
- J. Filliozat (1955). "Sanskrit as Language of Communication". Annals of the Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute. Bhandarkar Oriental Research Institute. 36 (3/4): 179–189. JSTOR 44082954.
- Filliozat, Pierre-Sylvain (2004), "Ancient Sanskrit Mathematics: An Oral Tradition and a Written Literature", in Chemla, Karine; Cohen, Robert S.; Renn, Jürgen; et al. (eds.), History of Science, History of Text (Boston Series in the Philosophy of Science), Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, pp. 360–375, ISBN 978-1-4020-2320-0
- Pierre-Sylvain Filliozat (2000). The Sanskrit Language: An Overview : History and Structure, Linguistic and Philosophical Representations, Uses and Users. Indica. ISBN 978-81-86569-17-7.
- Benjamin W. Fortson, IV (2011). Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-1-4443-5968-8.
- Robert P. Goldman; Sally J Sutherland Goldman (2002). Devavāṇīpraveśikā: An Introduction to the Sanskrit Language. Center for South Asia Studies, University of California Press.
- Thomas V. Gamkrelidze; Vjaceslav V. Ivanov (2010). Indo-European and the Indo-Europeans: A Reconstruction and Historical Analysis of a Proto-Language and Proto-Culture. Part I: The Text. Part II: Bibliography, Indexes. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-081503-0.
- Thomas V. Gamkrelidze; V. V. Ivanov (1990). "The Early History of Indo-European Languages". Scientific American. Nature America. 262 (3): 110–117. Bibcode:1990SciAm.262c.110G. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0390-110. JSTOR 24996796.
- Jack Goody (1987). The Interface Between the Written and the Oral. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33794-6.
- Reinhold Grünendahl (2001). South Indian Scripts in Sanskrit Manuscripts and Prints: Grantha Tamil, Malayalam, Telugu, Kannada, Nandinagari. Otto Harrassowitz Verlag. ISBN 978-3-447-04504-9.
- Houben, Jan (1996). Ideology and status of Sanskrit: contributions to the history of the Sanskrit language. Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-10613-0.
- Hanneder, J. (2002). on "The Death of Sanskrit"". Indo-Iranian Journal. Brill Academic Publishers. 45 (4): 293–310. doi:10.1023/a:1021366131934.
- Hock, Hans Henrich (1983). Kachru, Braj B (ed.). "Language-death phenomena in Sanskrit: grammatical evidence for attrition in contemporary spoken Sanskrit". Studies in the Linguistic Sciences. 13:2.
- Barbara A. Holdrege (2012). Veda and Torah: Transcending the Textuality of Scripture. State University of New York Press. ISBN 978-1-4384-0695-4.
- Michael C. Howard (2012). Transnationalism in Ancient and Medieval Societies: The Role of Cross-Border Trade and Travel. McFarland. ISBN 978-0-7864-9033-2.
- Dhanesh Jain; George Cardona (2007). The Indo-Aryan Languages. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-79711-9.
- Stephanie W. Jamison; Joel P. Brereton (2014). The Rigveda: 3-Volume Set, Volume I. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-972078-1.
- A. Berriedale Keith (1993). A history of Sanskrit literature. Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 978-81-208-1100-3.
- Damien Keown; Charles S. Prebish (2013). Encyclopedia of Buddhism. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-136-98595-9.
- Anne Kessler-Persaud (2009). Knut A. Jacobsen; et al. (eds.). Brill's Encyclopedia of Hinduism: Sacred texts, ritual traditions, arts, concepts. Brill Academic. ISBN 978-90-04-17893-9.
- Jared Klein; Brian Joseph; Matthias Fritz (2017). Handbook of Comparative and Historical Indo-European Linguistics: An International Handbook. Walter De Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-026128-8.
- Dalai Lama (1979). "Sanskrit in Tibetan Literature". The Tibet Journal. 4 (2): 3–5. JSTOR 43299940.
- Winfred Philipp Lehmann (1996). Theoretical Bases of Indo-European Linguistics. Psychology Press. ISBN 978-0-415-13850-5.
- Donald S. Lopez Jr. (1995). "Authority and Orality in the Mahāyāna" (PDF). Numen. Brill Academic. 42 (1): 21–47. doi:10.1163/1568527952598800. hdl:2027.42/43799. JSTOR 3270278.
- Mahadevan, Iravatham (2003). Early Tamil Epigraphy from the Earliest Times to the Sixth Century A.D. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0-674-01227-1.
- Malhotra, Rajiv (2016). The Battle for Sanskrit: Is Sanskrit Political or Sacred, Oppressive or Liberating, Dead or Alive?. Harper Collins. ISBN 978-9351775386.
- J. P. Mallory; Douglas Q. Adams (1997). Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-884964-98-5.
- Mallory, J. P. (1992). "In Search of the Indo-Europeans / Language, Archaeology and Myth". Praehistorische Zeitschrift. Walter de Gruyter GmbH. 67 (1). doi:10.1515/pz-1992-0118. ISSN 1613-0804.
- Colin P. Masica (1993). The Indo-Aryan Languages. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-29944-2.
- Michael Meier-Brügger (2003). Indo-European Linguistics. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-017433-5.
- Michael Meier-Brügger (2013). Indo-European Linguistics. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-089514-8.
- Matilal, Bimal (2015). The word and the world : India's contribution to the study of language. New Delhi, India Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-565512-4. OCLC 59319758.
- Maurer, Walter (2001). The Sanskrit language: an introductory grammar and reader. Surrey, England: Curzon. ISBN 978-0-7007-1382-0.
- J. P. Mallory; D. Q. Adams (2006). The Oxford Introduction to Proto-Indo-European and the Proto-Indo-European World. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-928791-8.
- V. RAGHAVAN (1965). "Sanskrit". Indian Literature. Sahitya Akademi. 8 (2): 110–115. JSTOR 23329146.
- MacDonell, Arthur (2004). A History Of Sanskrit Literature. Kessinger Publishing. ISBN 978-1-4179-0619-2.
- Sir Monier Monier-Williams (2005). A Sanskrit-English Dictionary: Etymologically and Philologically Arranged with Special Reference to Cognate Indo-European Languages. Motilal Banarsidass. ISBN 978-81-208-3105-6.
- Tim Murray (2007). Milestones in Archaeology: A Chronological Encyclopedia. ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-57607-186-1.
- Ramesh Chandra Majumdar (1974). Study of Sanskrit in South-East Asia. Sanskrit College.
- Nedi︠a︡lkov, V. P. (2007). Reciprocal constructions. Amsterdam Philadelphia: J. Benjamins Pub. Co. ISBN 978-90-272-2983-0.
- Oberlies, Thomas (2003). A Grammar of Epic Sanskrit. Berlin New York: Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-014448-2.
- Petersen, Walter (1912). "Vedic, Sanskrit, and Prakrit". Journal of the American Oriental Society. American Oriental Society. 32 (4): 414–428. doi:10.2307/3087594. ISSN 0003-0279. JSTOR 3087594.
- Sheldon Pollock (2009). The Language of the Gods in the World of Men: Sanskrit, Culture, and Power in Premodern India. University of California Press. ISBN 978-0-520-26003-0.
- Pollock, Sheldon (2001). "The Death of Sanskrit". Comparative Studies in Society and History. Cambridge University Press. 43 (2): 392–426. doi:10.1017/s001041750100353x. JSTOR 2696659.
- V. RAGHAVAN (1968). "Sanskrit: Flow of Studies". Indian Literature. Sahitya Akademi. 11 (4): 82–87. JSTOR 24157111.
- Colin Renfrew (1990). Archaeology and Language: The Puzzle of Indo-European Origins. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-38675-3.
- Louis Renou; Jagbans Kishore Balbir (2004). A history of Sanskrit language. Ajanta. ISBN 978-8-1202-05291.
- A. M. Ruppel (2017). The Cambridge Introduction to Sanskrit. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-08828-3.
- Salomon, Richard (1998). Indian Epigraphy: A Guide to the Study of Inscriptions in Sanskrit, Prakrit, and the other Indo-Aryan Languages. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-535666-3.
- Salomon, Richard (1998). Indian Epigraphy: A Guide to the Study of Inscriptions in Sanskrit, Prakrit, and the other Indo-Aryan Languages. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-535666-3.
- Salomon, Richard (1995). on the Origin of the Early Indian Scripts". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 115 (2): 271–279. doi:10.2307/604670. JSTOR 604670.
- Salomon, Richard (1998). Indian Epigraphy: A Guide to the Study of Inscriptions in Sanskrit, Prakrit, and the Other Indo-Aryan Languages. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-509984-3.
- Salomon, Richard (1995). on the Origin of the Early Indian Scripts". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 115 (2): 271–279. doi:10.2307/604670. JSTOR 604670.
- Malati J. Shendge (1997). The Language of the Harappans: From Akkadian to Sanskrit. Abhinav Publications. ISBN 978-81-7017-325-0.
- Seth, Sanjay (2007). Subject lessons: the Western education of colonial India. Durham, NC: Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0-8223-4105-5.
- Staal, Frits (1986), The Fidelity of Oral Tradition and the Origins of Science, Mededelingen der Koninklijke Nederlandse Akademie von Wetenschappen, Amsterdam: North Holland Publishing Company
- Staal, J. F. (1963). "Sanskrit and Sanskritization". The Journal of Asian Studies. Cambridge University Press. 22 (3): 261–275. doi:10.2307/2050186. JSTOR 2050186.
- Angus Stevenson; Maurice Waite (2011). Concise Oxford English Dictionary. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-960110-3.
- Southworth, Franklin (2004), Linguistic Archaeology of South Asia, Routledge, ISBN 978-1-134-31777-6
- Philipp Strazny (2013). Encyclopedia of Linguistics. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-135-45522-4.
- Paul Thieme (1958). "The Indo-European Language". Scientific American. Nature. 199 (4): 63–78. Bibcode:1958SciAm.199d..63T. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican1058-63. JSTOR 24944793.
- Peter van der Veer (2008). "Does Sanskrit Knowledge Exist?". Journal of Indian Philosophy. Springer. 36 (5/6): 633–641. doi:10.1007/s10781-008-9038-8. JSTOR 23497502.
- Umāsvāti, Umaswami (1994), That which is (Translator: Nathmal Tatia), Rowman & Littlefield, ISBN 978-0-06-068985-8
- Wayman, Alex (1965). "The Buddhism and the Sanskrit of Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit". Journal of the American Oriental Society. 85 (1): 111–115. doi:10.2307/597713. JSTOR 597713.
- Annette Wilke; Oliver Moebus (2011). Sound and Communication: An Aesthetic Cultural History of Sanskrit Hinduism. Walter de Gruyter. ISBN 978-3-11-024003-0.
- Whitney, W. D. (1885). "The Roots of the Sanskrit Language". Transactions of the American Philological Association. JSTOR. 16: 5–29. doi:10.2307/2935779. ISSN 0271-4442. JSTOR 2935779.
- Witzel, M (1997). Inside the texts, beyond the texts: New approaches to the study of the Vedas (PDF). Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.
- Jamison, Stephanie (2008). Roger D. Woodard (ed.). The Ancient Languages of Asia and the Americas. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-68494-1.
External links[edit]
| Sanskrit edition of Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia |
| For a list of words relating to Sanskrit, see the Sanskrit language category of words in Wiktionary, the free dictionary. |
| Wikibooks has more on the topic of: Sanskrit |
- INDICORPUS-31, 31 Sanskrit + dravidian dictionaries for Lingvo.
- Sanskrit Lessons (free online from the Linguistics Research Center at UT Austin)
- Samskrita Bharati, organisation supporting the usage of Sanskrit
- Sanskrit Documents—Documents in ITX format of Upanishads, Stotras etc.
- Sanskrit texts at Sacred Text Archive
- Sanskrit Manuscripts in Cambridge Digital Library
- Lexilogos Sanskrit Keyboard for writing Sanskrit on a computer.
'문화방' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Stabroek 시장 시계 (0) | 2020.02.18 |
|---|---|
| 기생충영화관람 (0) | 2020.02.16 |
| 진정한 기독교 – 요한 아른트 (0) | 2020.02.12 |
| 소망의 바다 (0) | 2020.02.12 |
| Europe, Middle East, & Far East (0) | 2020.02.10 |